Data Parsing
Split raw strings (JSON, log lines, free text) into structured JSON fields so downstream components can use them.
Key Terms
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| JSON parser | Built-in syntax for extracting keys from JSON payloads. |
| Grok parser | Regex-based syntax ideal for log parsing. |
| Structured | Data already arrives as clean key/value pairs. |
| Semi-structured | Has repeatable patterns that can be tokenized. |
| Unstructured | No reliable pattern; treated as a single blob. |
Prerequisites
- Decide which information you need and what the final structure should look like.
- Every raw payload is wrapped in
_Message;_Timestampis added automatically.
Getting Started
Choose the field to split
You can configure several rules, but each rule processes one field at a time.
Choose parser type
Supports JSON-format data splitting, custom text splitting, and Grok-parser splitting.
-
JSON-format split: when the target field is JSON, extract only the selected keys and convert them into top-level fields.
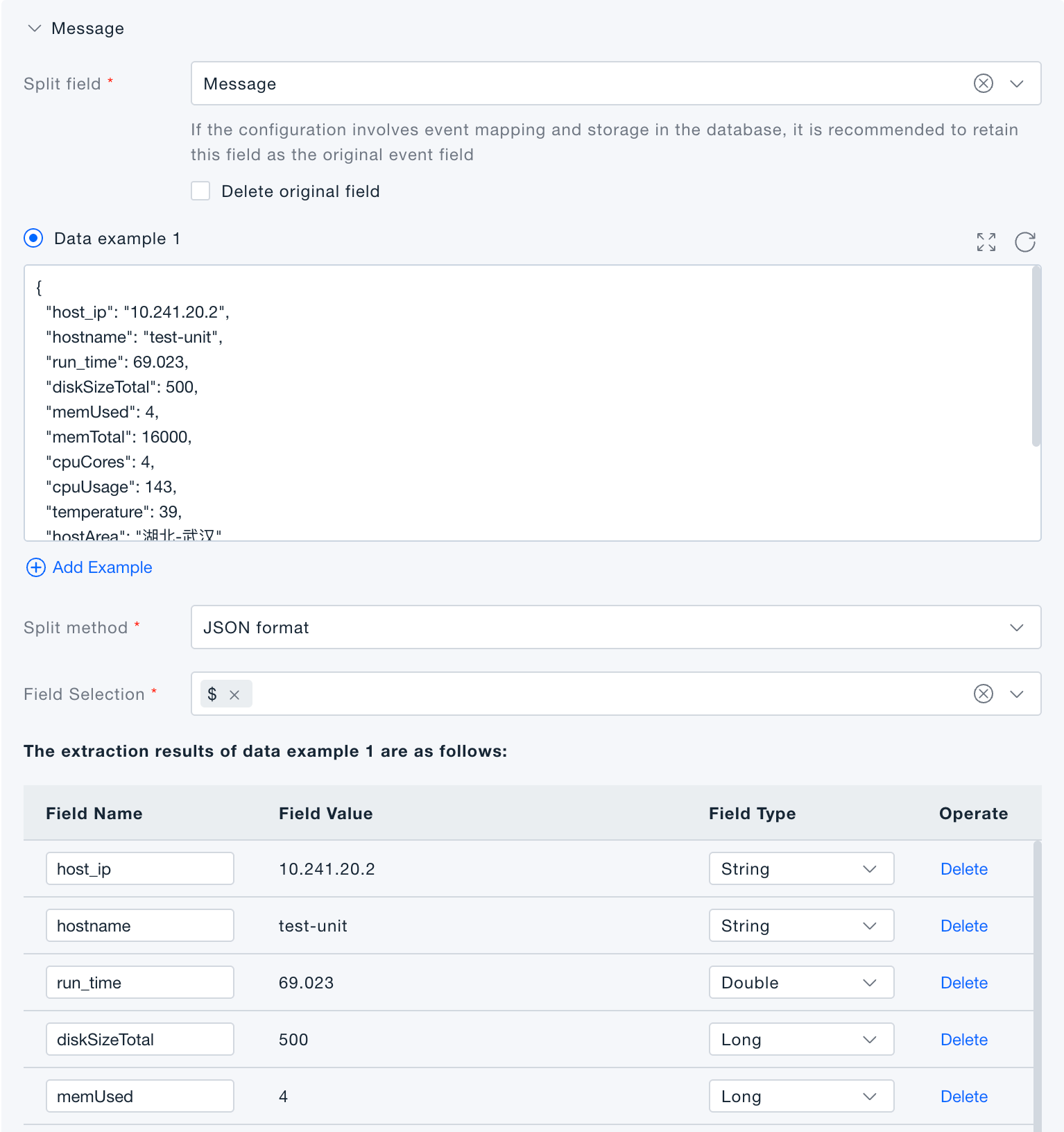
-
Custom text split: cut the data by a chosen delimiter; each resulting segment becomes an independent field.
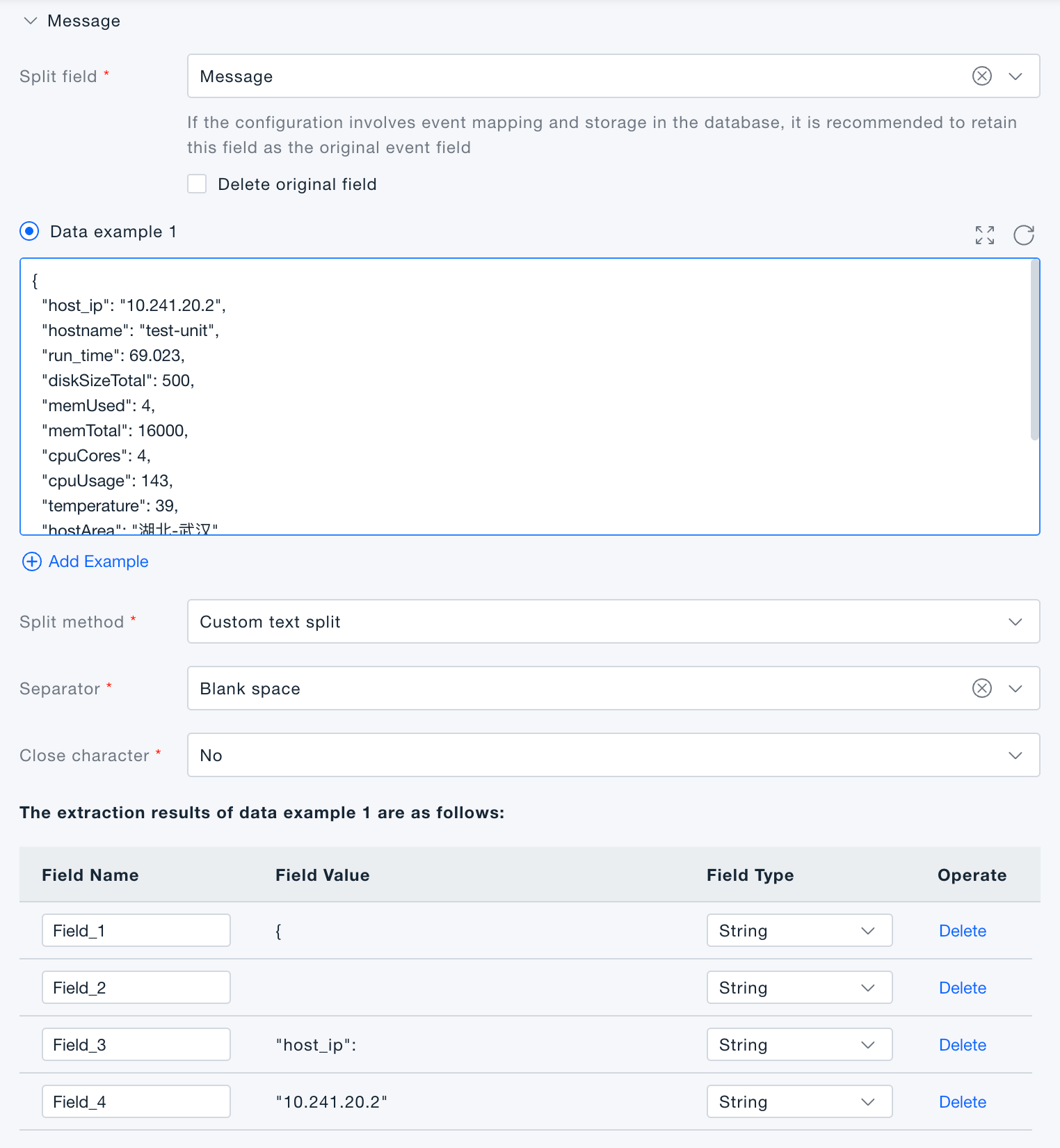
-
Grok parser: uses Grok syntax to split text data, ideal for parsing log text fields.
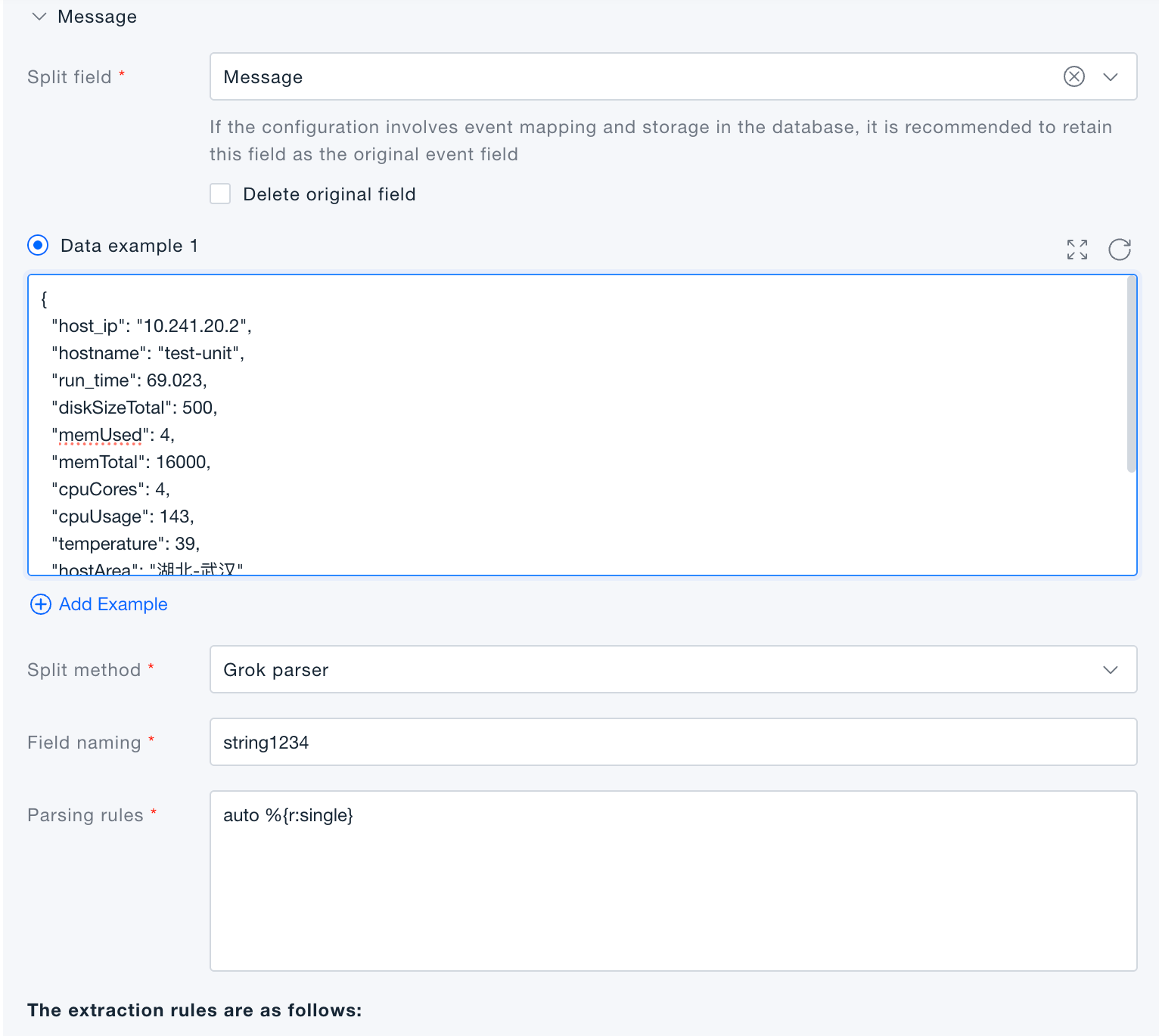
Verification
Click Execute Preview to review the results in the preview panel. (Preview simulates the transformation—no actual data is written to the platform.)
Grok Syntax Reference
Syntax Overview
%{Matcher:Extract:Filter}
- Matcher (required): a pattern or reference to another rule that describes the expected content
- Extract (optional): the destination field name for the captured text; if omitted, the match is performed but no value is stored
- Filter (optional): a transformation applied to the matched result
Supported Matchers
date("pattern")
Currently supported date formats:
| Date Format | pattern | Analysis results |
|---|---|---|
| 14:20:15 | HH:mm:ss | 22815000 |
| 02:20:15 PM | hh:mm:ss a | 22815000 |
| 11/10/2014 | dd/MM/yyyy | 1412956800000 |
| Thu Jun 16 08:29:03 2016 | EEE MMM dd HH:mm:ss yyyy | 1466036943000 |
| Tue Nov 1 08:29:03 2016 | EEE MMM d HH:mm:ss yyyy | 1477960143000 |
| 06/Mar/2013:01:36:30 +0900 | dd/MMM/yyyy:HH:mm:ss Z | 1468407336000 |
| 2016-11-29T16:21:36.431+0000 | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ | 1480436496431 |
| 2016-11-29T16:21:36.431+00:00 | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZZ | 1480407696431 |
| 06/Feb/2009:12:14:14.655 | dd/MMM/yyyy:HH:mm:ss.SSS | 1233893654655 |
| 2007-08-31 19:22:22.427 ADT | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS z | 1188598942427 |
| 2023-04-13 22:01:10 | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss | 1681394470000 |
| 2023/04/13 22:01:10 | yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss | 1681394470000 |
| 2023-04-13 22:01:10.211 | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS | 1681394470211 |
| 2023-04-13 22:01:10,211 | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS | 1681394470211 |
| 2023-Apr-20 09:49:18.813567 | yyyy-MMM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS | 1681955358000 |
| 13/Jul/2016:10:55:36 +0000 | dd/MMM/yyyy:HH:mm:ss Z | 1468407336000 |
| 2017-12-29T12:33:33.095243Z | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSSSSZ | 1514522013095 |
| 25 Apr 2023 10:16:52.612 | dd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss.SSS | 1682389012612 |
| 2016-06-15 7:53:33 | yyyy-MM-dd H:mm:ss | 1465948413000 |
| 08 Jan 17:55:41.572 | dd MMM HH:mm:ss.SSS | 1673171741572 |
| 05-04 10:30:49.710 | MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS | 1683167449710 |
regex("pattern")
- When using the pattern as a regular expression, please be mindful of escaping special characters.
- Regular expression syntax: Regular Expression – Syntax | Rookie Tutorial (runoob.com)
notSpace
Match any non-whitespace character. Equivalent to [^\f\n\r\t\v].
boolean("truePattern", "falsePattern")
The value is true when matching truePattern, and false when matching falsePattern.
uuid
Match a UUID in 64-bit format, e.g.: 8fb9c71d-817b-4a6a-8fea-546860f258b5.
mac
Match a MAC address.
ipv4
Match an IPv4 address.
ipv6
Match an IPv6 address.
ip
Equivalent to IPv4 or IPv6.
port
Match a server port in the range of 1-65535.
word
Match A-Z, a-z, 0-9 characters, including the _ (underscore) character.
data
- Matches any string, including spaces and line breaks. Equivalent to the regular expression
[\s\S]*?, and should be used when none of the above patterns are suitable.
The ? symbol used by default in this matcher enables lazy mode, i.e., minimal matching; it switches to greedy mode, i.e., maximal matching, only when this matcher is placed last.
Supported Filters
number
Parse the match into a double-precision number.
integer
Parse the match into an integer.
boolean
Parse the strings 'true' and 'false' into case-insensitive boolean values.
nullIf("value")
If the matched value equals the provided value, return null.
lowercase
Convert all to lowercase.
uppercase
Convert all to uppercase.
json
Convert a JSON string into a key-value map structure, supporting two syntax formats:
1. %{data:aaa:json}
2. %{data::json}
url
Parse the URL and return all tokenized components (domain, query parameters, port, etc.) in a JSON object.
Grok syntax:
r %{data:mapping:url}
Parse target:
http://localhost:8082/deploy/config/collection/log/dataprocessing
{
"mapping": {
"url": "http://localhost:8082/deploy/config/collection/log/dataprocessing",
"scheme": "http",
"host": "localhost",
"port": 8082,
"path": "/deploy/config/collection/log/dataprocessing"
}
}
keyvalue
| String Form | Key-Value Notation | Result | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| key=valueStr | %{data::keyvalue} | {"key": "valueStr"} | Single k:v split |
| key:valueStr | %{data::keyvalue(":")} | {"key": "valueStr"} | |
| key=valueStr | %{data::keyvalue("=")} | {"key": "valueStr"} | |
| key1: value1,key2: value2 | %{data::keyvalue(": ", ",")} | {key1: value1, key2: value2} | Multiple k:v split |
Sub-rule Description
- Helper rules, also known as sub-rules, serve as supplementary references to parsing rules in theory.
- The extract (i.e., alias) of a sub-rule will also be displayed as the field name after extraction.
- Sub-rules can reference other sub-rules.
- It is important to note that while parsing rules can reference sub-rules, sub-rules cannot reference the parsing expressions of the main rules to prevent infinite recursive loops.
eg:
Log source:
com.bonree.one.Task.class INFO 2023-04-20 15:02:02 log
Parsing rule:
auto %{r:single}
Sub-rule:
r %{data:className} %{word:level} %{ot:timestamp} log
ot %{date("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"):timestampgg}
Parsing result:
{
"single": "com.bonree.one.Task.class INFO 2023-04-20 15:02:02 log",
"timestampgg": 1681974122000,
"level": "INFO",
"className": "com.bonree.one.Task.class",
"timestamp": "2023-04-20 15:02:02"
}