CMDB Entities Extraction
Extract asset entities and their relationships from third-party data and inject them into the ONE CMDB, powering all downstream analytics.
Every SDK, SmartAgent, SmartGate, and ONE platform capability is built on top of the CMDB; keeping it accurate is critical.
Key Terms
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Asset Entity | An object worth monitoring: host, service, application, disk, pod, etc. |
| Entity Model | The abstract template: “Host” is a model. |
| Entity Instance | A concrete example: host-10.241.1.1 is an instance of the Host model. |
| Relation Model | Abstract link between models: Host contains Disk. |
| Relation Instance | Concrete link: host-10.241.1.1 contains Disk-Dev01. |
| Required Relation | Parent-child existence dependency (Service contains Service-Instance). |
| Optional Relation | Ad-hoc link that can be added later (Service calls Service). |
Prerequisites
- Identify which entities and relationships exist in the raw data.
- Place any required parsing steps before this component.
Getting Started
ONE offers two strategies:
| Strategy | When to Use |
|---|---|
| CMDB Extraction | Fixed entity models; you only need to create instances. |
| Automated CMDB Registration | Entity models must be created on-the-fly from field values. |
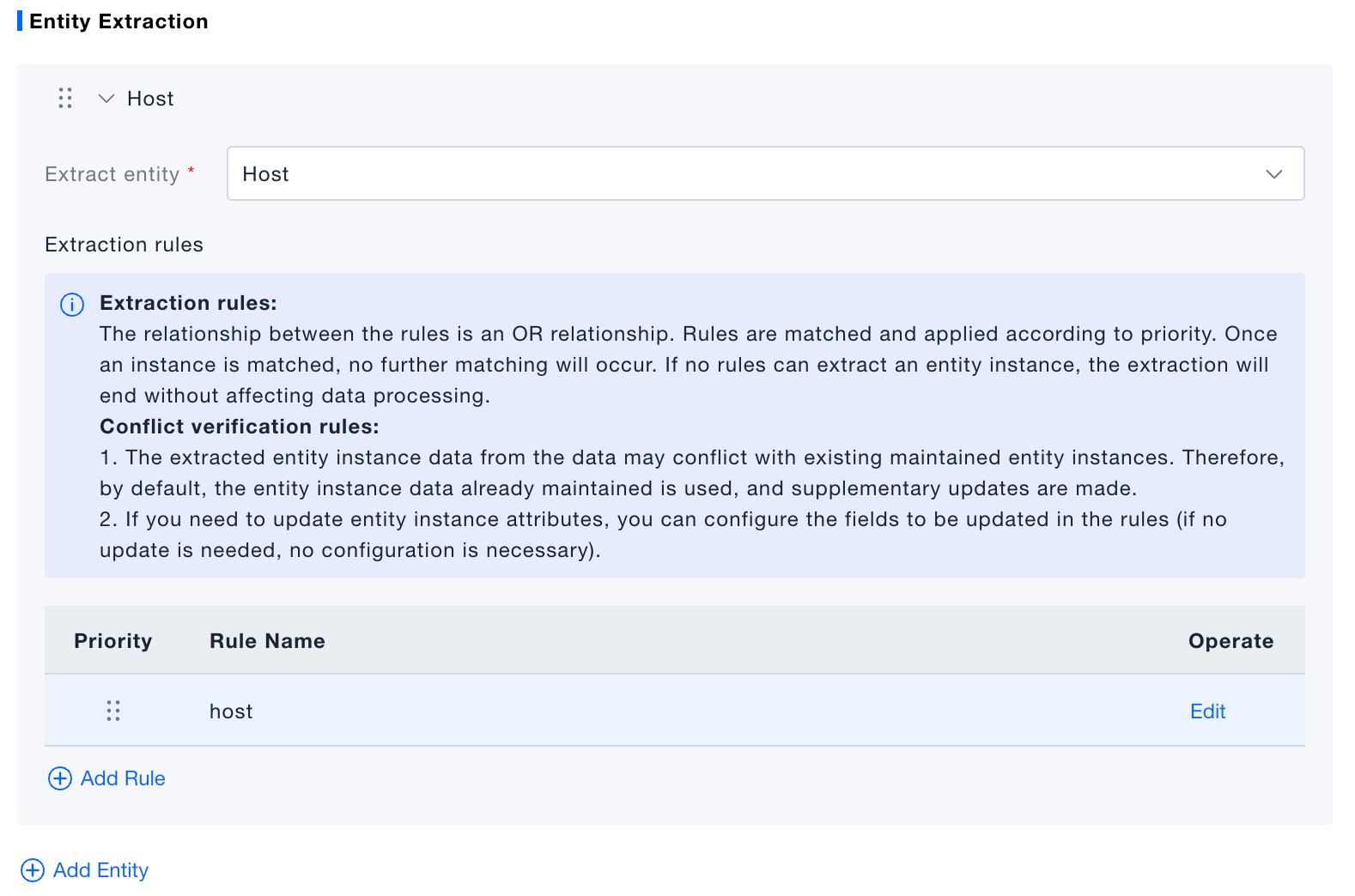
CMDB Extraction
- Add rules (one component can hold many).
- Rules run top-down; first match wins.
- Multiple rules for the same entity are prioritized—higher priority stops further matching.
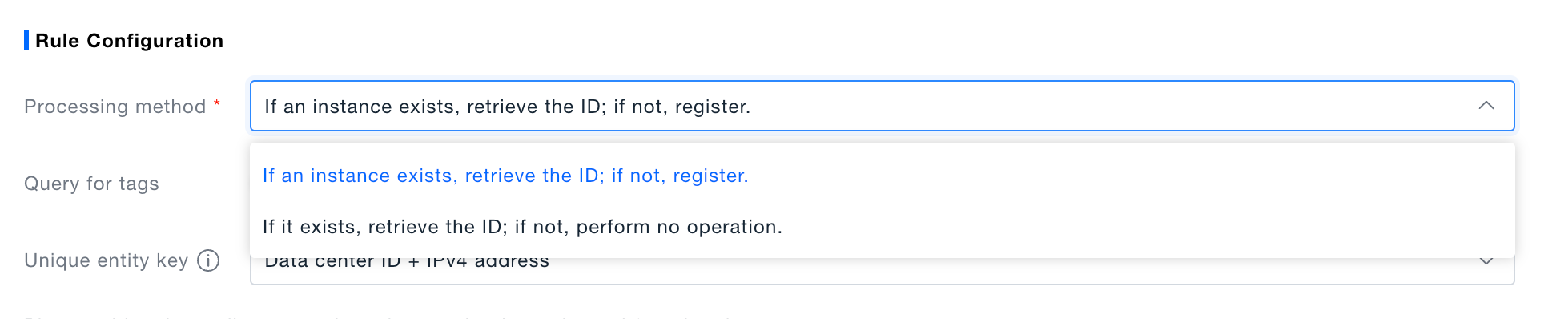
- Choose processing mode
- “Get ID if exists, else register” – compares unique key; creates missing instances.
- “Get ID if exists, else skip” – compares unique key; continues if no match.
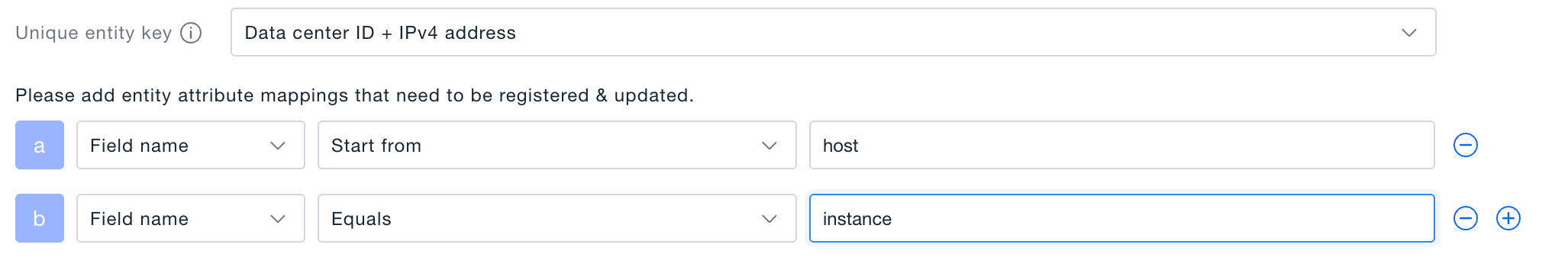
- Define unique key & match condition
- Unique key fields are used to decide if an instance already exists.
- Match conditions (AND logic) determine whether the rule should run at all.
- Map attributes
- Back-fill – pull current CMDB values into the data stream.
- Update strategy (only when registering):
– Fill empty (recommended) – update only null attributes.
– Overwrite – replace existing attributes with collected data.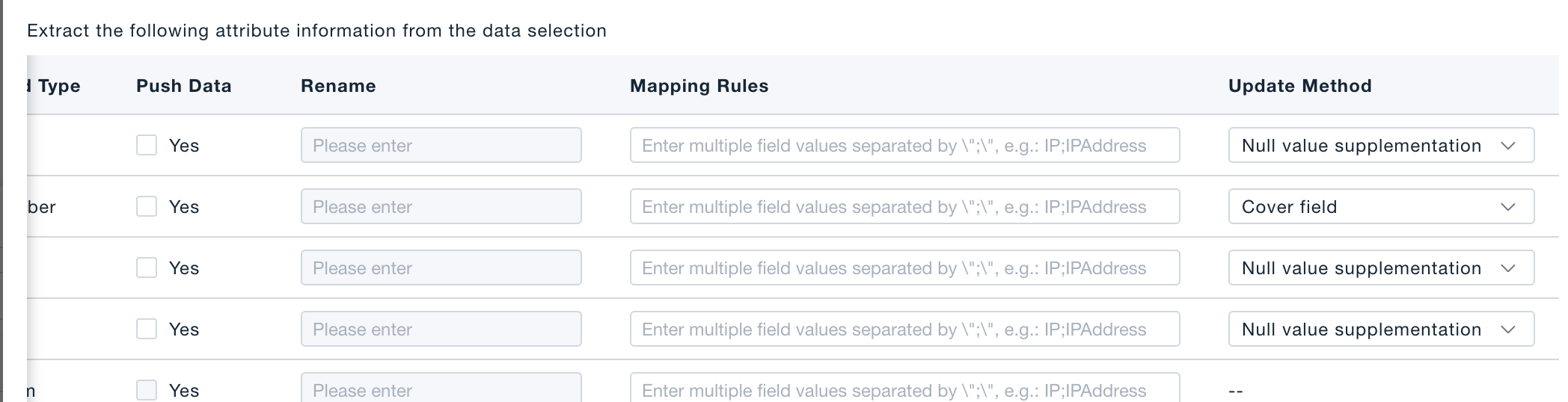
- Save rule and, if needed, add relationship definitions.
When both ends of a configured relation are found in_CMDB, the component automatically creates the relation instance.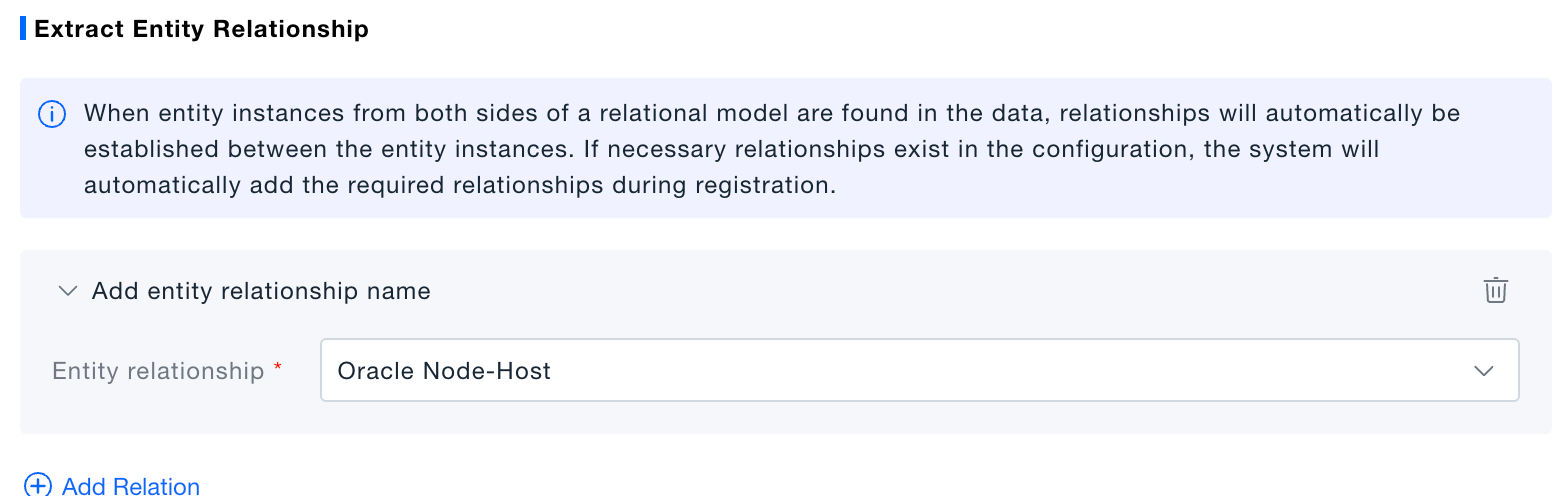
Automated CMDB Registration
-
Choose entity category.
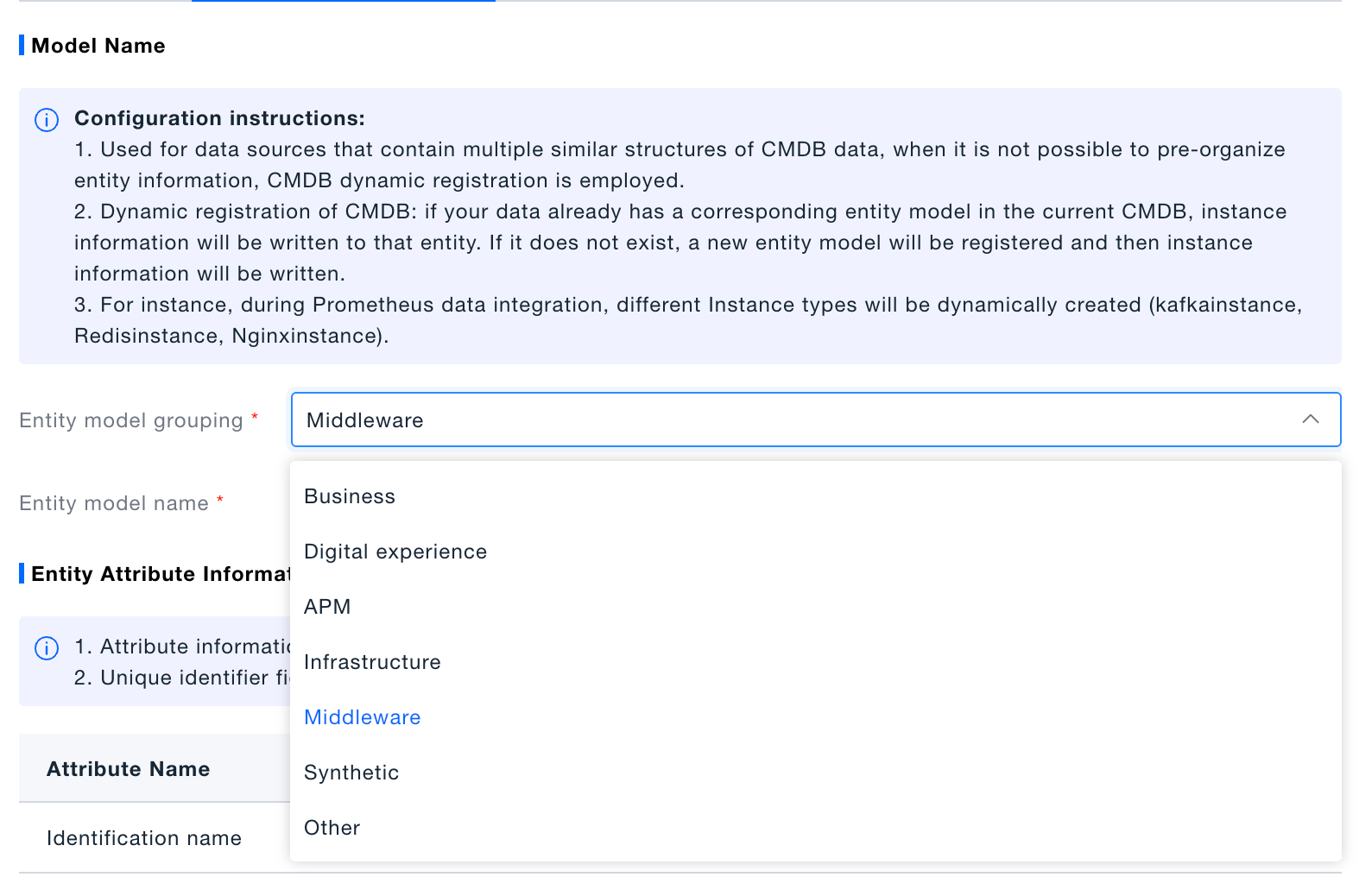
-
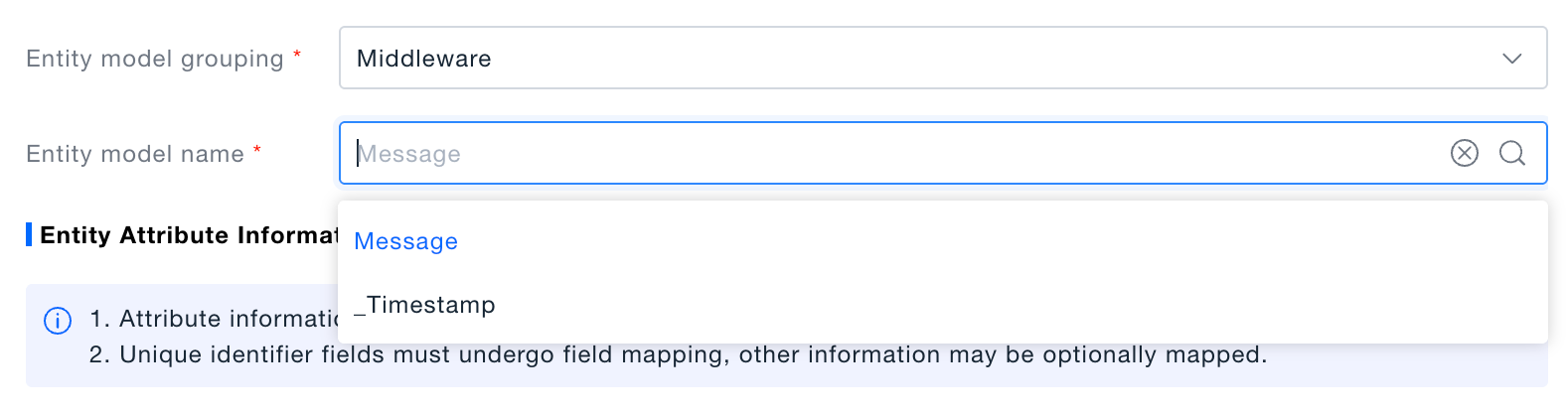
Select the field whose value becomes the entity name.
- If the entity already exists, only the instance is registered.
- If the entity does not exist, it is created under the chosen category first.
-
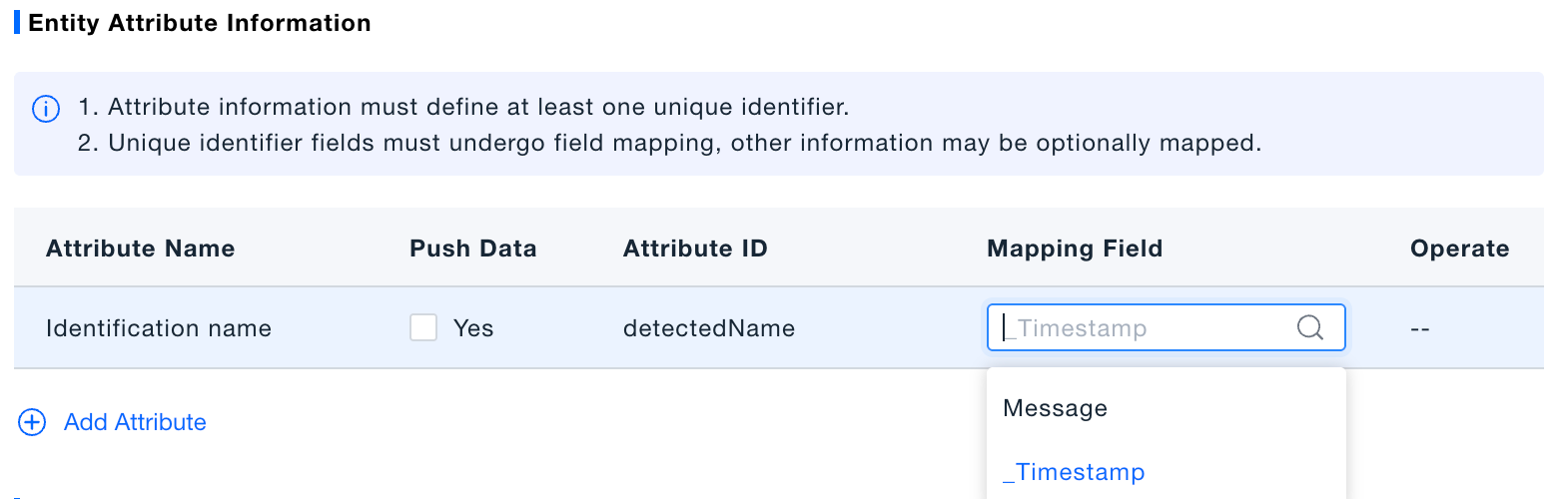
Map attributes.
-
Save rule and optionally add relationships.
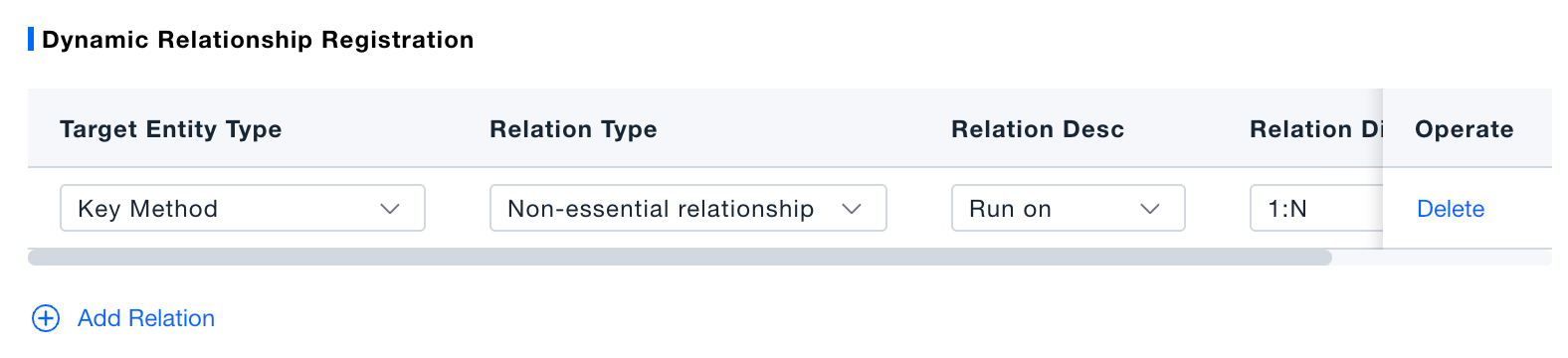
Verification
A successful extraction injects a _CMDB object into the record. If _CMDB contains a non-empty Model key, the extraction completed.