Convergent Strategy
Prerequisites
Functional Menu: Has access to the Convergence Strategy function menu.
Operational Permissions: Has create, read/write, or read-only permissions for Alert Configuration.
Data Permissions: Has at least one resource domain in an environment.
Data Prerequisites: Alert rules are configured and alerts are being generated.
Overview
The convergence strategy intelligently merges, compresses, and correlates multi-source alerts, transforming massive chaotic alerts into precisely localized problems. Based on algorithms such as AI root cause analysis and topology correlation, this strategy automatically identifies intrinsic relationships between alerts, converging alerts with the same feature set into unified problems. It fundamentally resolves alert storms, achieving an intelligent transition from "noisy alerts" to "precise problems."
Value
- Intelligent Alert Management
- By leveraging AI-driven root cause convergence and topological analysis, the system automatically identifies and merges duplicate alerts.
- It effectively reduces alert volume by over 90%, significantly improving the signal-to-noise ratio of alerts.
- This prevents alert storms from overwhelming operational teams and minimizes redundant efforts.
- Precise Root Cause Localization
- Using correlation analysis based on topological relationships, the system rapidly pinpoints the root cause node of issues.
- It distinguishes between superficial alerts and fundamental root cause alerts through converged entity hierarchies.
- The generated root cause problems include visual topological diagrams that intuitively display issue propagation paths.
- Exponential Improvement in Operational Efficiency
- It liberates operational personnel from screening massive alerts, allowing them to focus on core problem resolution.
- The system shortens fault localization time, reducing Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) by over 60%.
- Through continuous knowledge base accumulation, it forms a virtuous cycle of increasing intelligence with usage.
Use Cases
-
Distributed Fault Localization in Microservices Architecture
In complex microservice call chains, a single service failure may trigger cascading alerts. The convergence strategy uses topological correlation analysis to automatically identify the root cause service, converging dozens of related alerts into a single core issue.
-
Alert Storm Suppression in Infrastructure Monitoring
When server clusters experience anomalies, they often generate large volumes of duplicate alerts. Based on device topology and alert characteristics, the convergence strategy enables intelligent deduplication and grouping to generate consolidated issues, maintaining clarity and usability of the problem list.
-
Unified Monitoring in Multi-Cloud Environments
In hybrid cloud and multi-cloud scenarios, the convergence strategy transcends cloud platform boundaries. By leveraging logical relationships between applications and services, it achieves cross-platform alert unification and root cause analysis.
Operational Scenario
- Query: When users need to query records in the convergence strategy list, they can filter based on the convergence strategy name and enable/disable status in the search box.
- Create: When users need to define a convergence strategy, they can click the Create button to create a new convergence strategy.
- Delete: When certain convergence strategies are no longer applicable, users can click the Delete button in the operation column, or select multiple items and click the Delete button above the list.
- Copy: When users need to define a convergence strategy and want to modify it based on an existing strategy, they can click the Copy button to duplicate the convergence strategy.
- Edit: When users need to adjust convergence rules, they can locate the already created strategy and click the Edit button to modify the convergence strategy.
- Enable/Disable: When a created convergence strategy needs to take effect, users can click the enable button; when it no longer needs to be effective, they can click the disable button to perform the operation.
Get Started
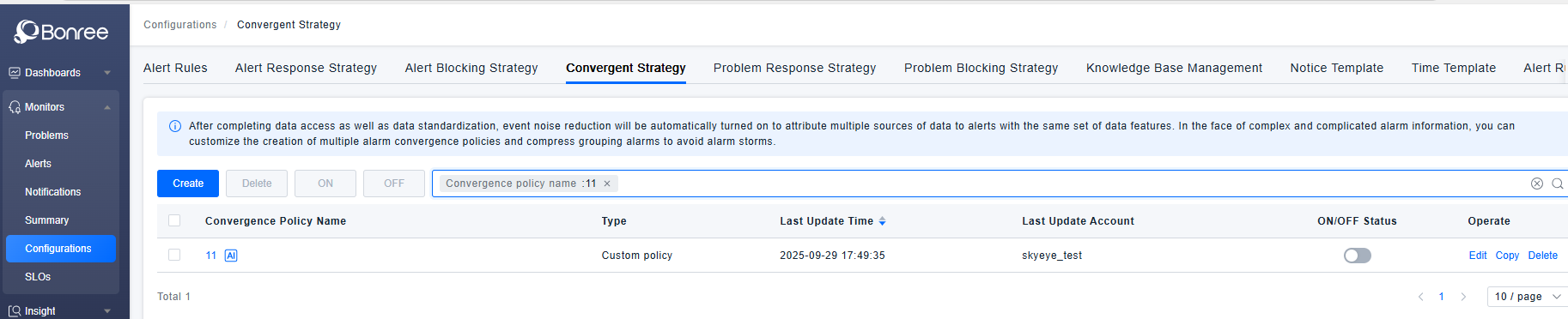
Convergent Strategy List
- Log in to Bonree ONE.
- Select Intelligent Alerting > Alert Configuration > Convergence Strategies.
- The system supports querying, creating, editing, copying, enabling, disabling, and deleting convergence strategies.
- The list provides the following fields: Convergence Strategy Name, Type, Last Updated Time, Last Updated Account, Enable/Disable Status, and Action Column.
- Note: The AI Root Cause Convergence strategy is a built-in strategy that cannot be deleted but can be edited, enabled, or disabled. Additionally, the AI Root Cause Convergence strategy requires an AI Intermediate License to be enabled or edited. If the AI Root Cause Convergence strategy is enabled, all other convergence strategies will become ineffective regardless of their enable/disable status.
Convergent Strategy Details
-
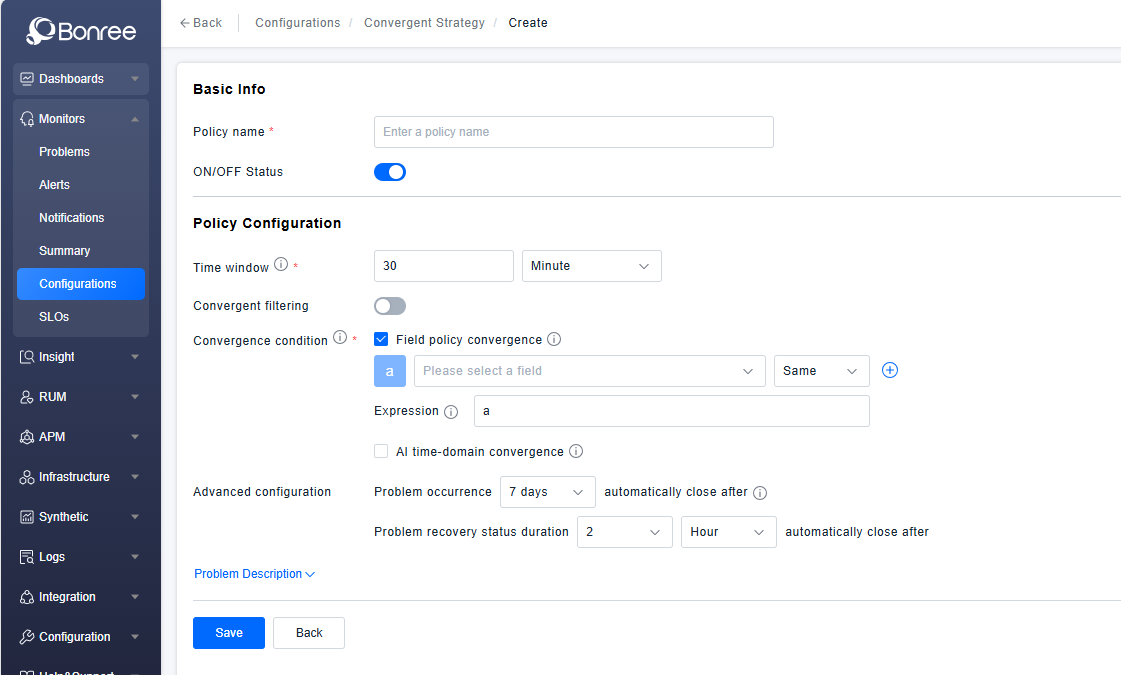
It includes Basic Information and Strategy Configuration.
-
Basic Information requires filling in the strategy name and enable/disable status, which is enabled by default.
-
Strategy Configuration includes Time Window, Convergence Filter, Convergence Conditions, Alert Configuration, and Problem Description Configuration.
-
Time Window defines the time relationship for alerts converged under this strategy as 30 minutes, meaning alerts within 30-minute intervals are converged.
-
Convergence Filter allows filtering based on alert fields to define the scope of alerts where the convergence strategy takes effect.
-
Convergence Conditions include
- Field Exact Match: Specific field values of alerts are identical.
- Field Similarity: Specific field values of alerts are similar.
- AI Temporal Convergence: Alerts exhibit similar temporal characteristics in their state changes or related time nodes after generation.
-
Advanced Configuration allows defining the lifecycle of problems generated by this strategy, i.e., the rules for closing problems. It can be configured to automatically close problems after a specified duration from their occurrence or after they have remained in a resolved state for a defined period.