Data Processing
Log data flows into the data processing pipeline stage after preprocessing and enters the corresponding processing pipeline by matching filter conditions.
Getting Started
Processing Pipeline List
Data is only processed by a single pipeline; the highest priority pipeline takes effect. Each pipeline can use a maximum of 20 processors. A single Grok processor can use up to 10 parsing rules. The platform automatically identifies data sources and loads the corresponding data processing pipelines, requiring no manual user configuration. Users can click on the Processing Pipeline Library to view which pipelines the platform supports.
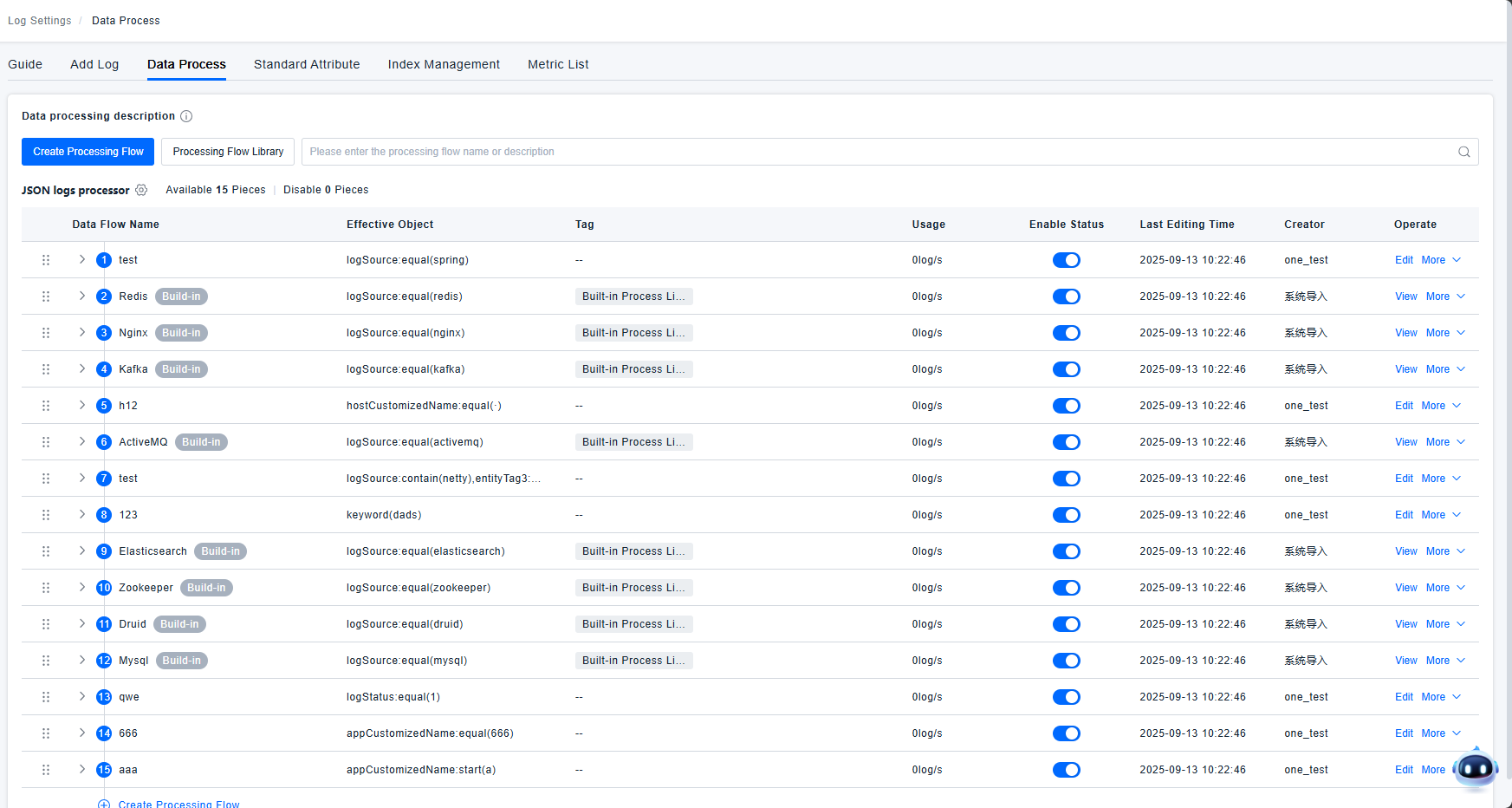
JSON Parsing
The platform automatically parses JSON-formatted data; no configuration is needed.
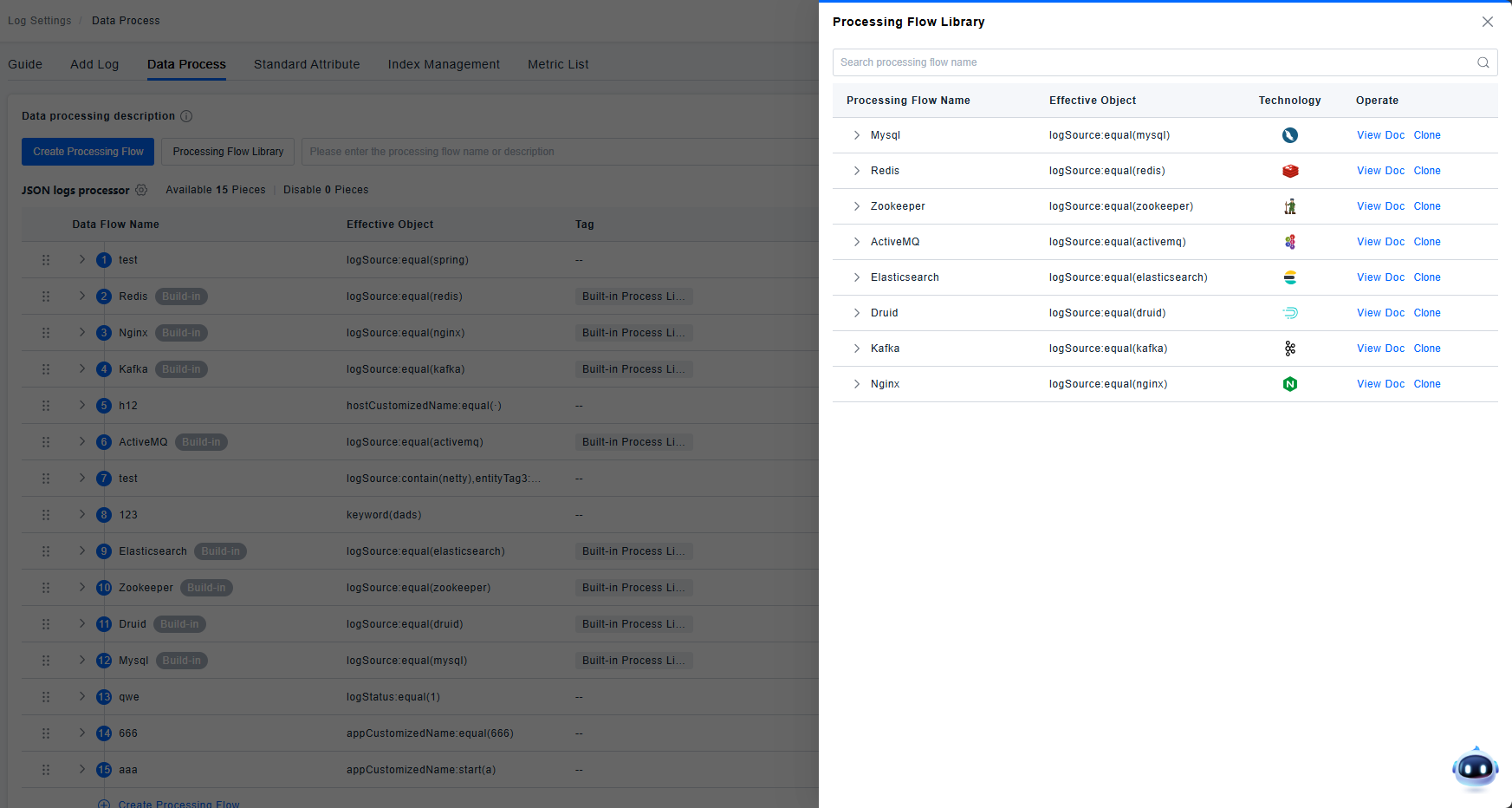
Processing Pipeline Library
The platform automatically identifies data sources and loads the corresponding data processing pipelines, requiring no manual user configuration. Data processing pipelines are composed of processors and inherited data processing flows, working together to parse logs.
Creating a New Processing Pipeline
When the default processing pipelines do not meet user requirements, a new pipeline can be created. A processing pipeline consists of processors or nested processing pipelines.
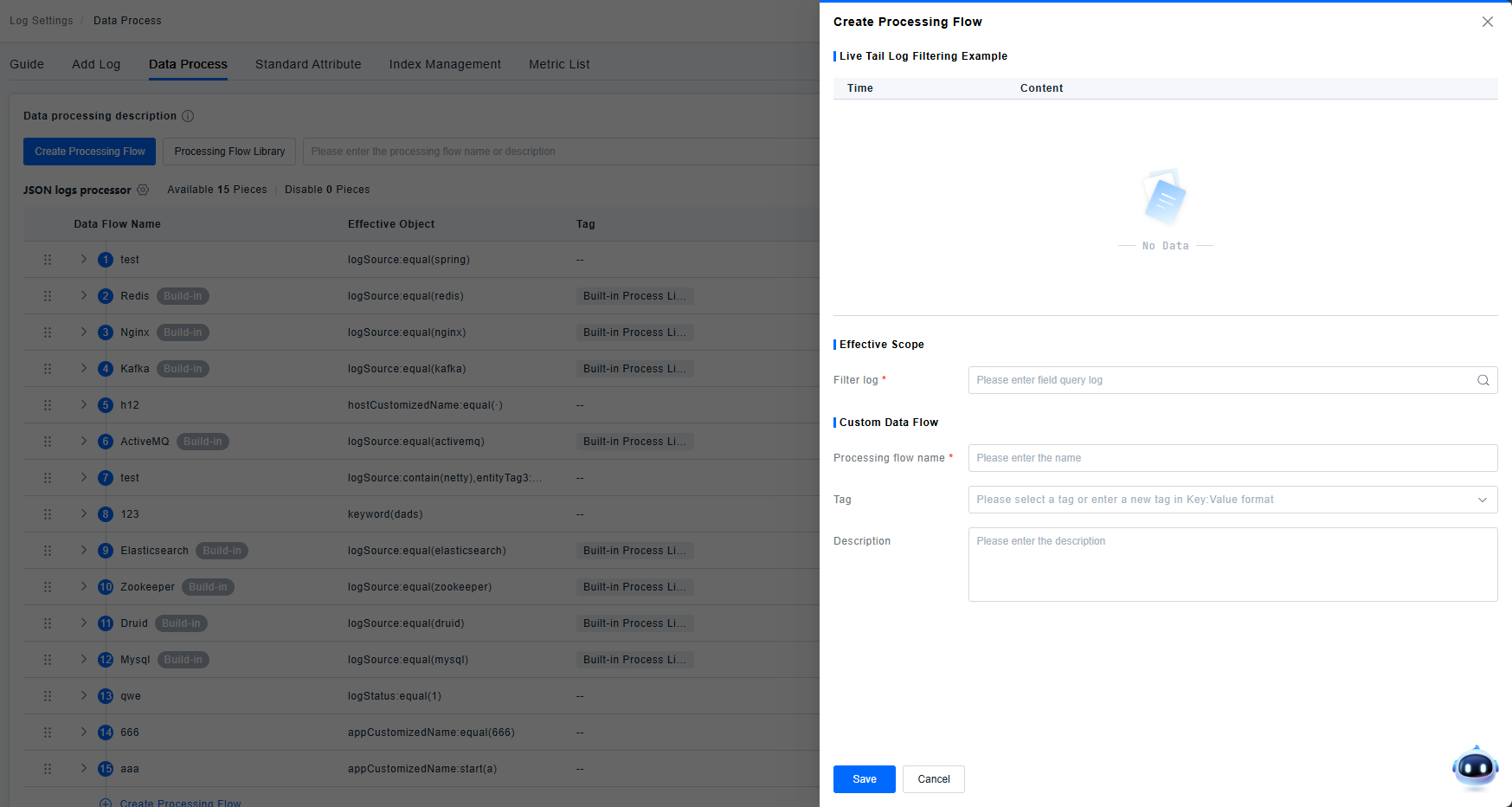
There are two types of processing pipelines: platform-built-in (read-only) and user-defined (custom).
Read-only pipelines support the following actions: View, Query Logs, Log Tail, Move, Clone, Enable/Disable.
| Action | Effect |
|---|---|
| View | Displays the pipeline details page; all information is grayed out and unmodifiable. |
| Query Logs | Opens a new page for log querying. |
| Log Tail | Opens a new page for LiveTail. |
| Move | Displays the move dialog. |
| Clone | Creates a new, identical pipeline based on the current one, but with edit permissions. The old pipeline is automatically disabled, and the new one is enabled and placed directly after the cloned pipeline. |
| Enable/Disable | When enabled, the rule is active; when disabled, the rule is inactive. |
Custom pipelines support the following actions: Edit, Query Logs, Log Tail, Move, Clone, Delete, Enable/Disable.
| Action | Effect |
|---|---|
| Edit | Opens the pipeline details page where information can be modified. |
| Query Logs | Opens a new page for log querying. |
| Log Tail | Opens a new page for LiveTail. |
| Move | Displays the move dialog. |
| Clone | Creates a new, identical pipeline based on the current one. The old pipeline is not automatically disabled. The new pipeline is placed below the original one with lower priority. |
| Delete | Clicking prompts a confirmation dialog. Upon confirmation, the rule is deleted. New data will no longer be processed by this rule (accepts a propagation delay, recommended not to exceed 3 minutes). |
| Enable/Disable | When enabled, the rule is active; when disabled, the rule is inactive. |
Processors
The platform supports Grok Parser, Remapper, User-Agent Parser, URL Parser, GeoIP Parser, Date Remapper, Body Remapper, Status Remapper, Service Remapper, Category Processor, Arithmetic Processor, String Builder Processor, Trace Id Remapper, and Lookup Processor.
There are two types of processors: platform-built-in (read-only) and user-defined (custom).
Read-only processors support the action: View. Displays the processor details page; all information is grayed out and unmodifiable.
Custom processors support the actions: Edit, Clone, Move, Delete, Enable/Disable.
| Action | Effect |
|---|---|
| Edit | Opens the processor details page where information can be modified. |
| Clone | Creates a new, identical processor based on the current one. The old processor is not disabled. The new processor is placed below the original one with lower priority. |
| Move | Allows moving the processor to a different processing pipeline (nesting). Direct drag-and-drop is also supported. |
| Delete | Clicking prompts a confirmation dialog. Upon confirmation, the rule is deleted. New data will no longer be processed by this processor (accepts a propagation delay, recommended not to exceed 3 minutes). |
| Enable/Disable | When enabled, the rule is active; when disabled, the rule is inactive. |
Grok Parser
Grok: Parses fields based on GROK syntax for field extraction. By default, it extracts fields from the body field. The "Extract from" option in advanced settings allows specifying any field for extraction. For complex nested rules, sub-rules can be used.
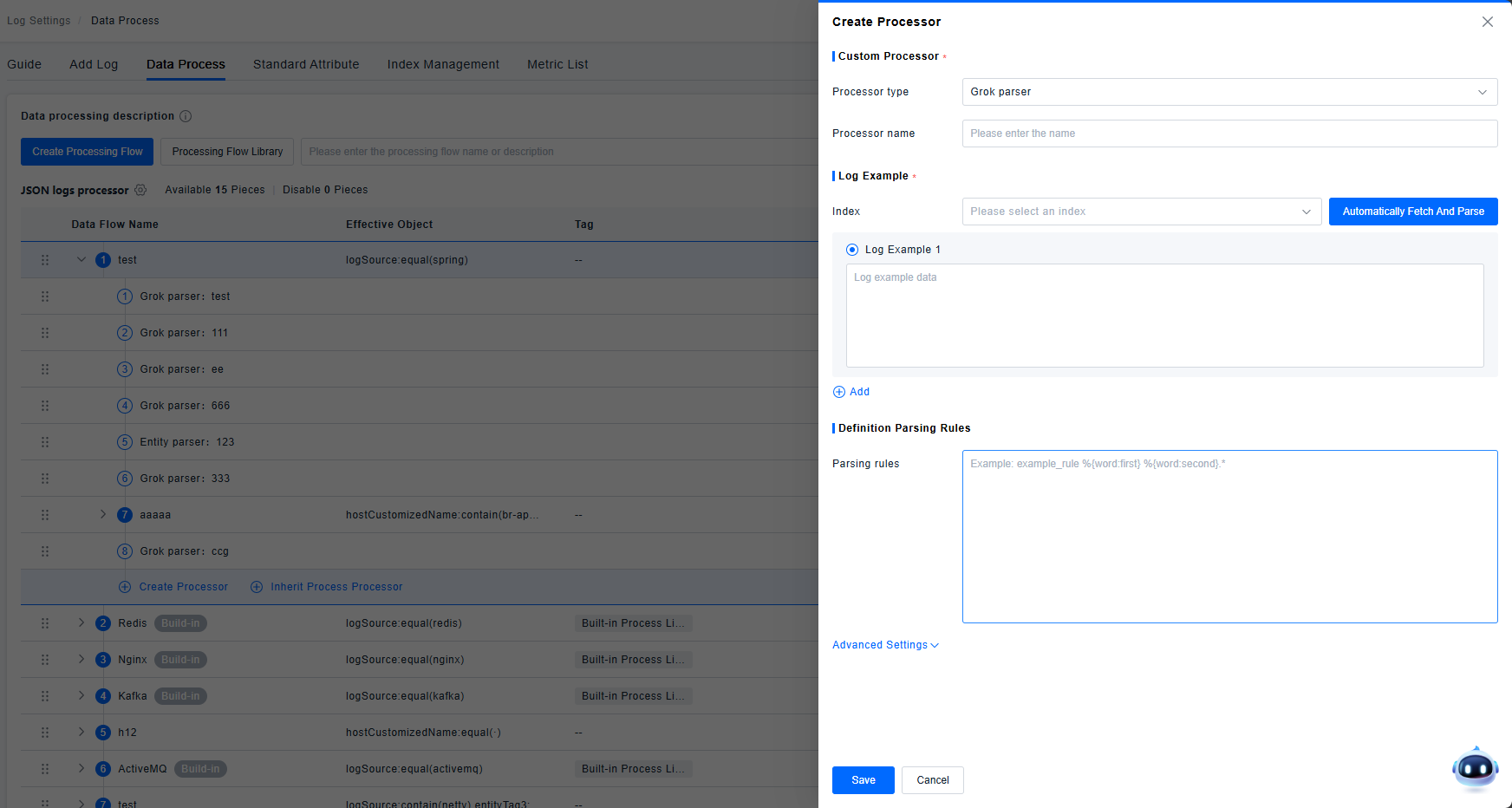
Supports automatic parsing. The system automatically fetches newly ingested logs and suggests corresponding parsing rules. If no logs are ingested, it prompts: "We haven't found recent indexes matching this processing pipeline." If logs are visible in LiveTail but cannot be parsed automatically, verify if these logs are stored in an index, as they might be excluded by an exclusion processor.
Logs matching the rule are flagged as a rule match; those not matching are flagged as a rule mismatch.
Remapper
Remaps an existing attribute/tag key to a new attribute path/tag key.
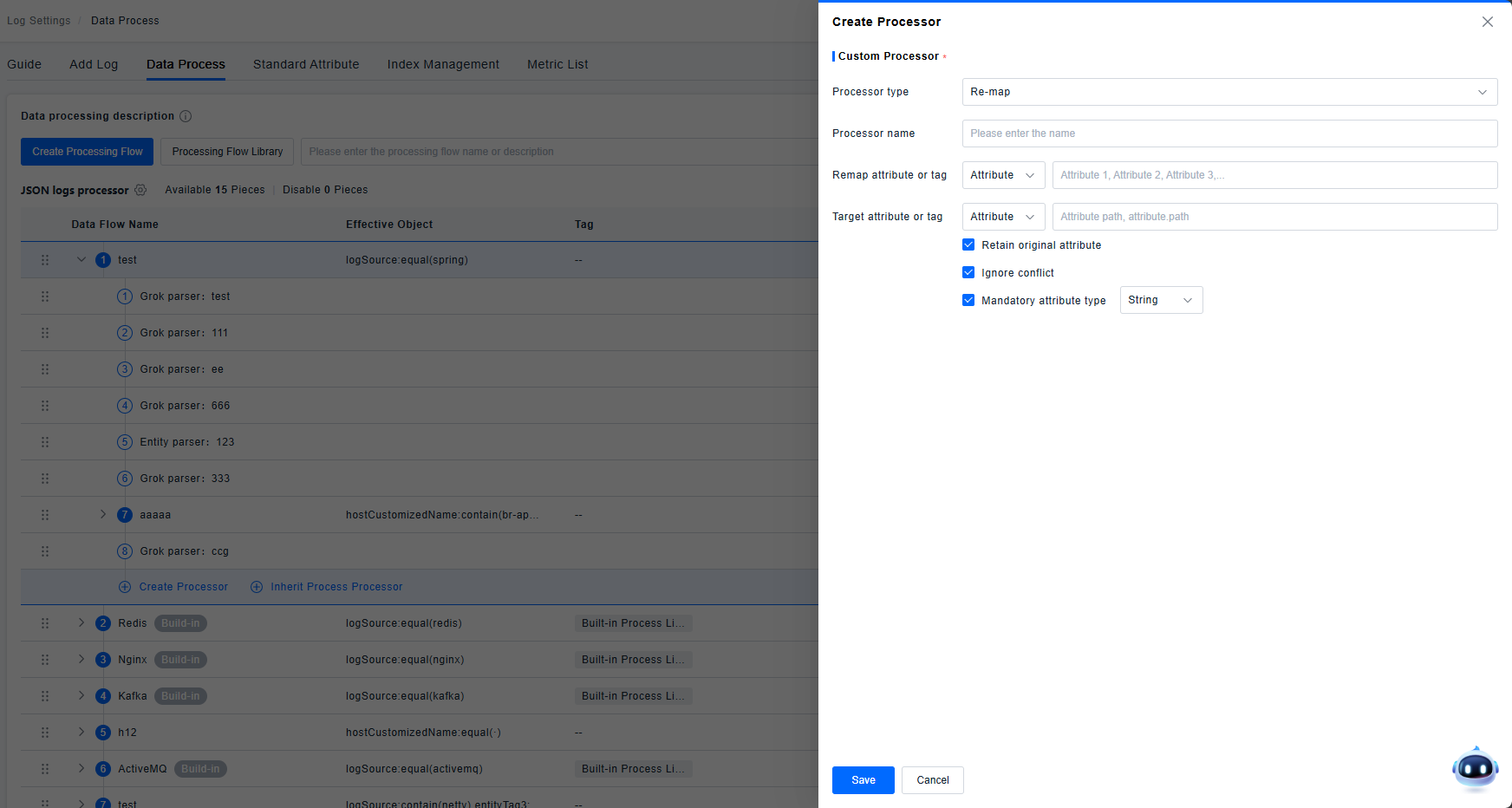
- Keep Source Attribute: If enabled, the original attribute remains saved and visible. If disabled, the original attribute is not saved or displayed.
- Ignore Conflicts: If enabled, proceeds with replacement logic; if disabled, does not replace in case of conflict.
- Force Attribute Type Change: Supports changing type to string, integer, or double. Default is string, and this option is enabled by default.
- When remapping to a tag, only "Keep Source Attribute" and "Ignore Conflicts" configurations are supported.
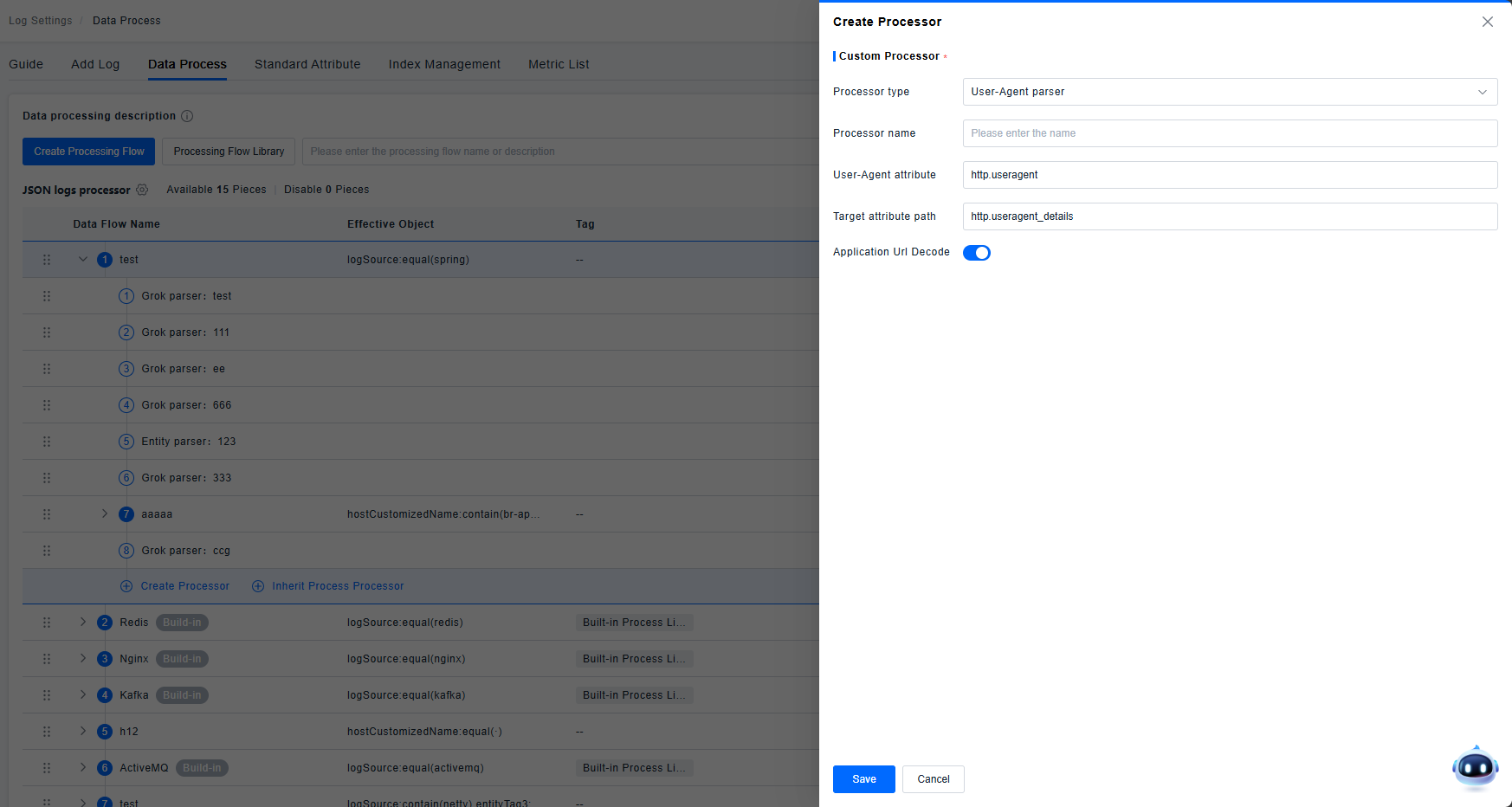
User-Agent Parser
Parses the User-Agent field according to its specification to identify information such as location and device.
Supports configuring UrlDecode. UrlDecode is an encoding processing function that decodes URL-encoded strings. Strings encoded via urlencode can be decoded using UrlDecode.
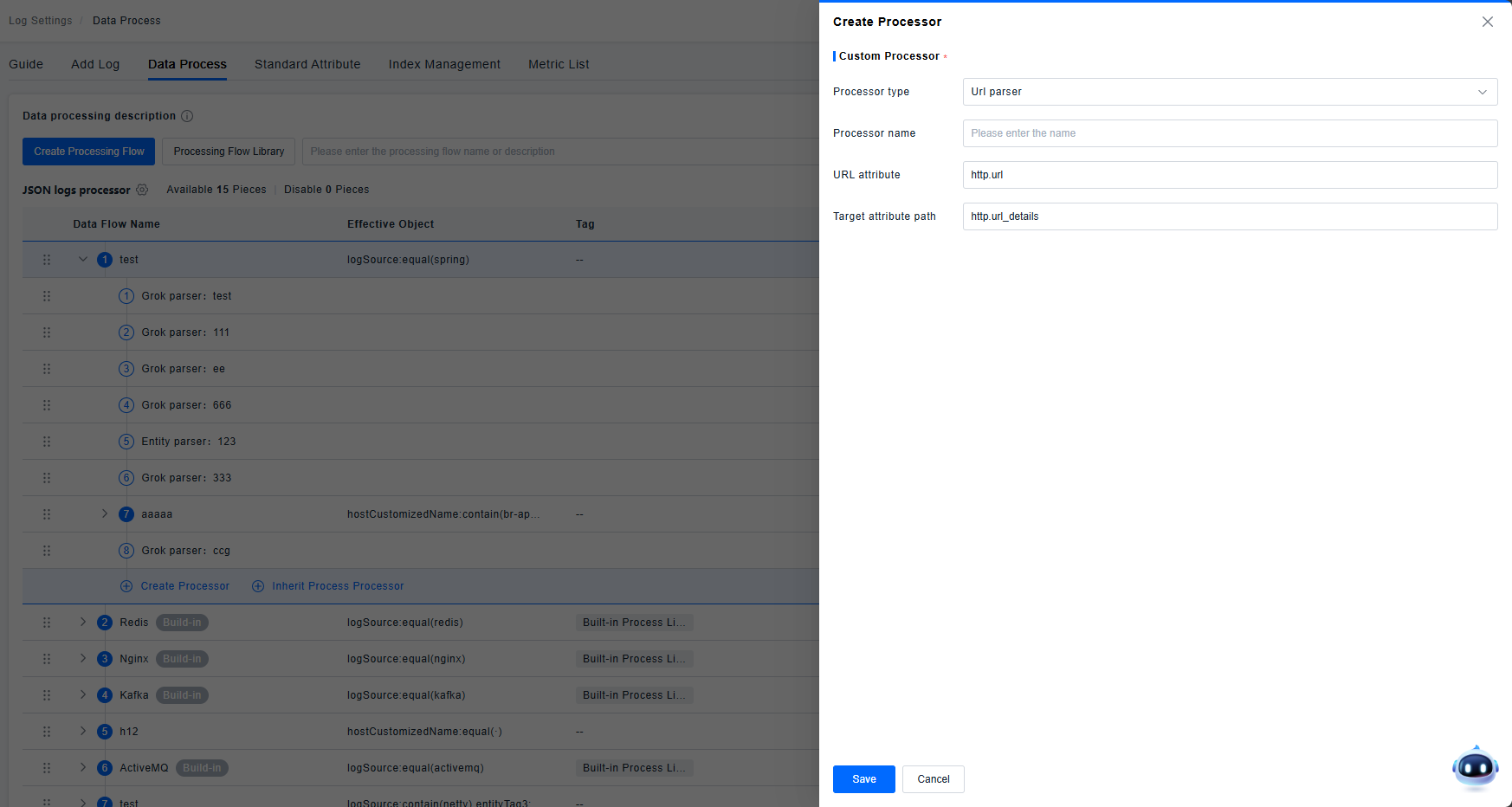
URL Parser
Used for URL parsing. Interprets the URL field based on its specification to identify scheme, host, path, queryString, etc.
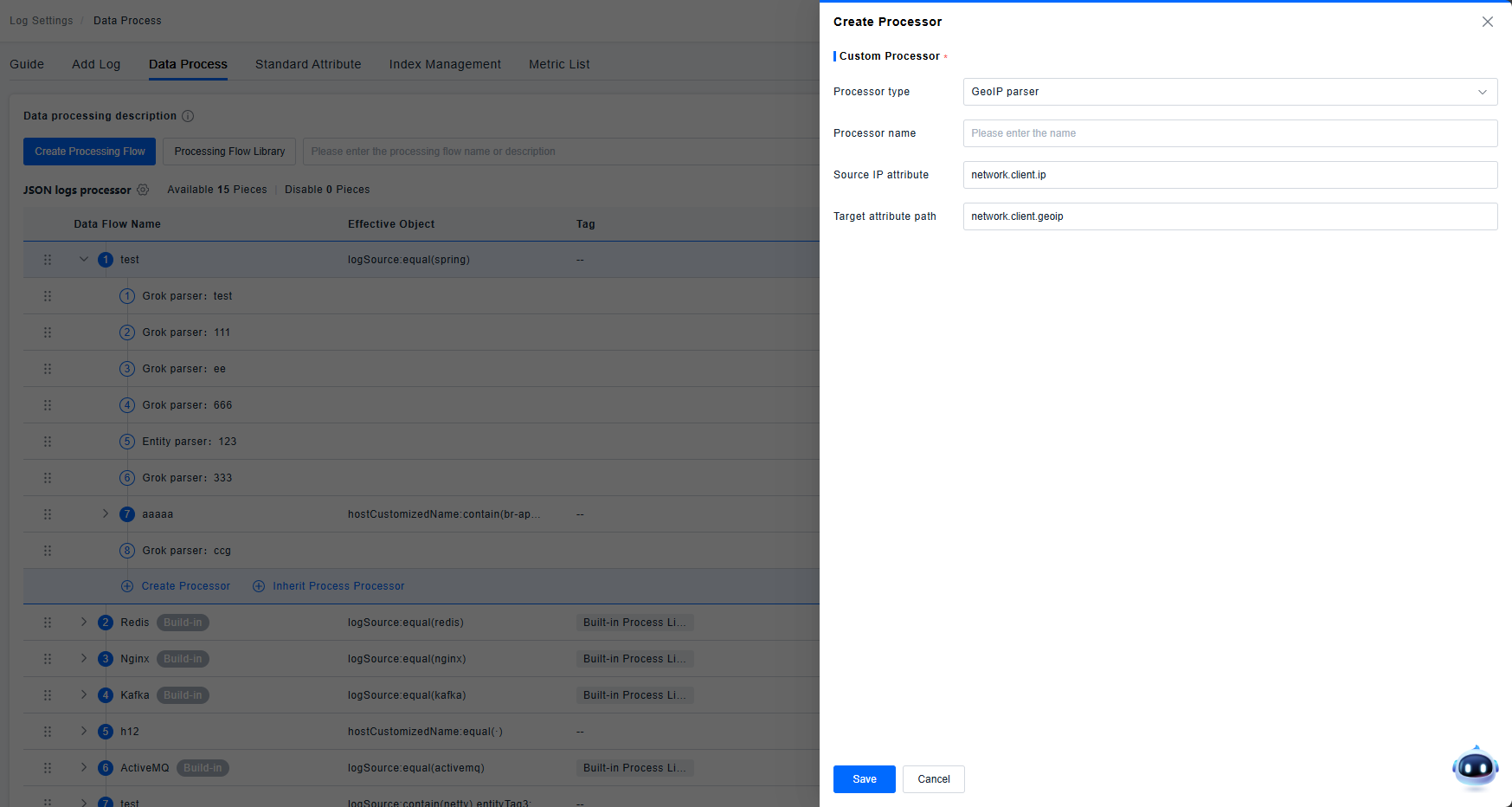
GeoIP Parser
Used for IP address parsing. Takes an IP address attribute and extracts country, region, or city information into the target attribute path.
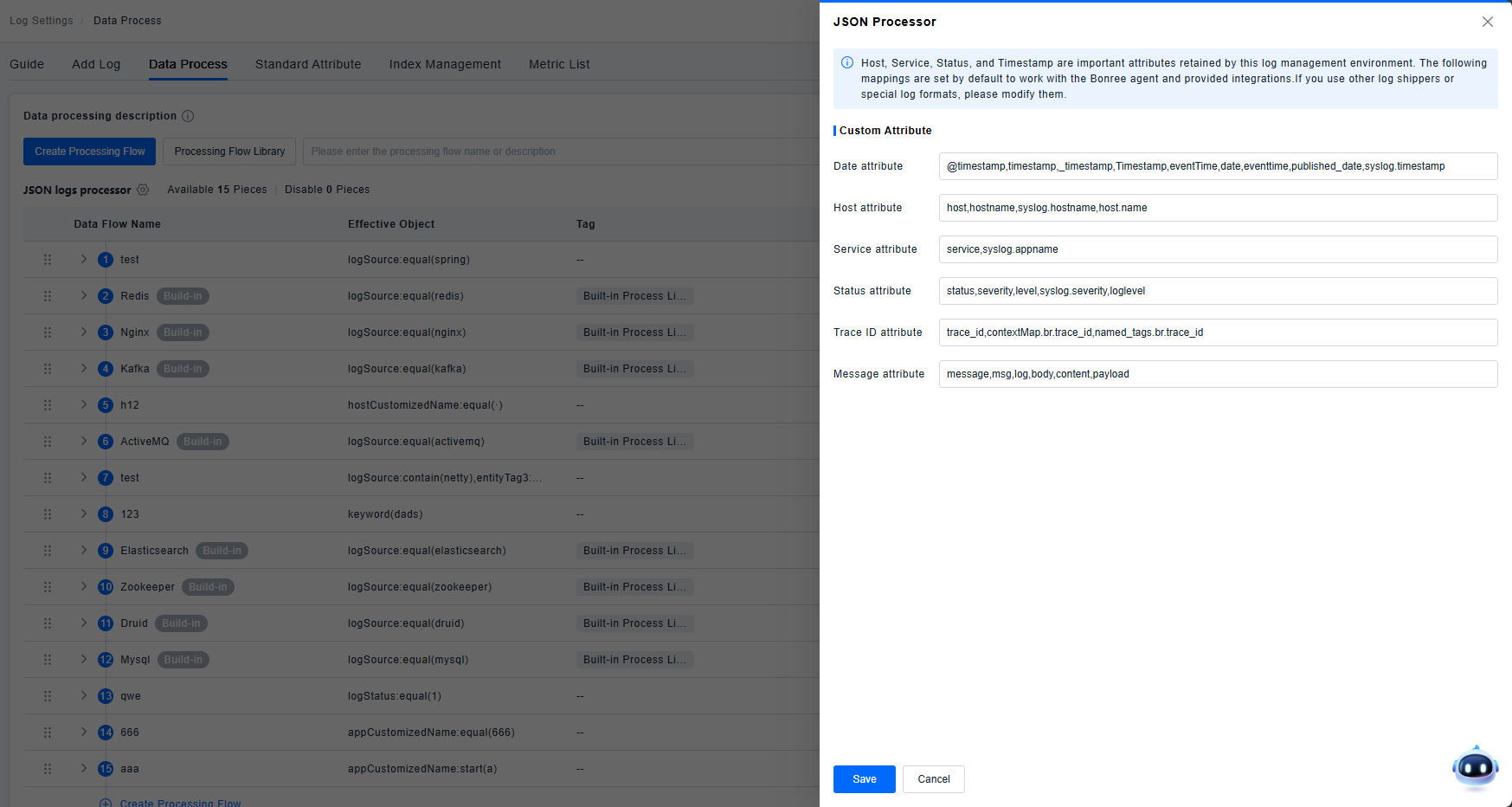
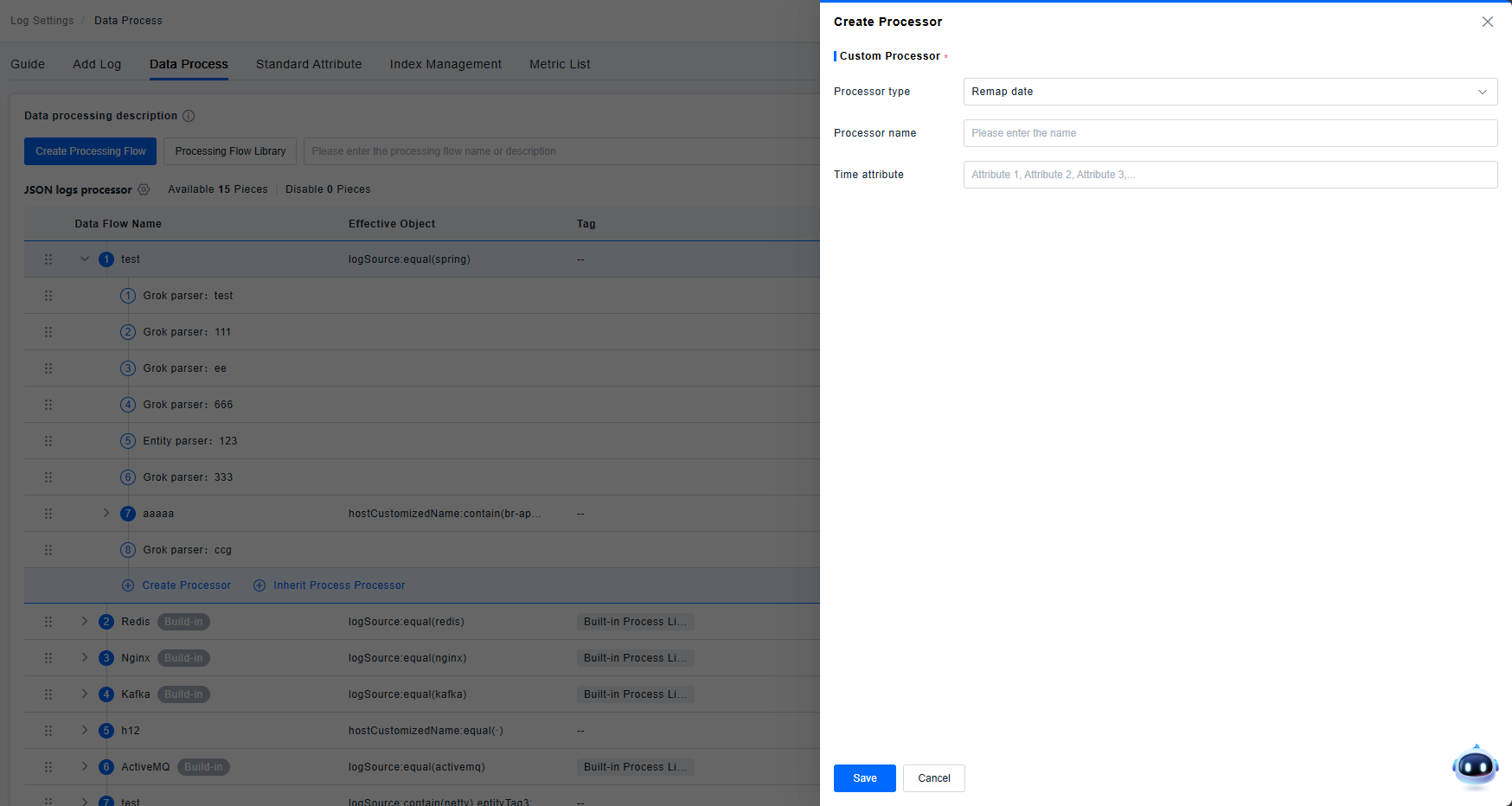
Date Remapper
Maps a specified attribute to the timestamp field.
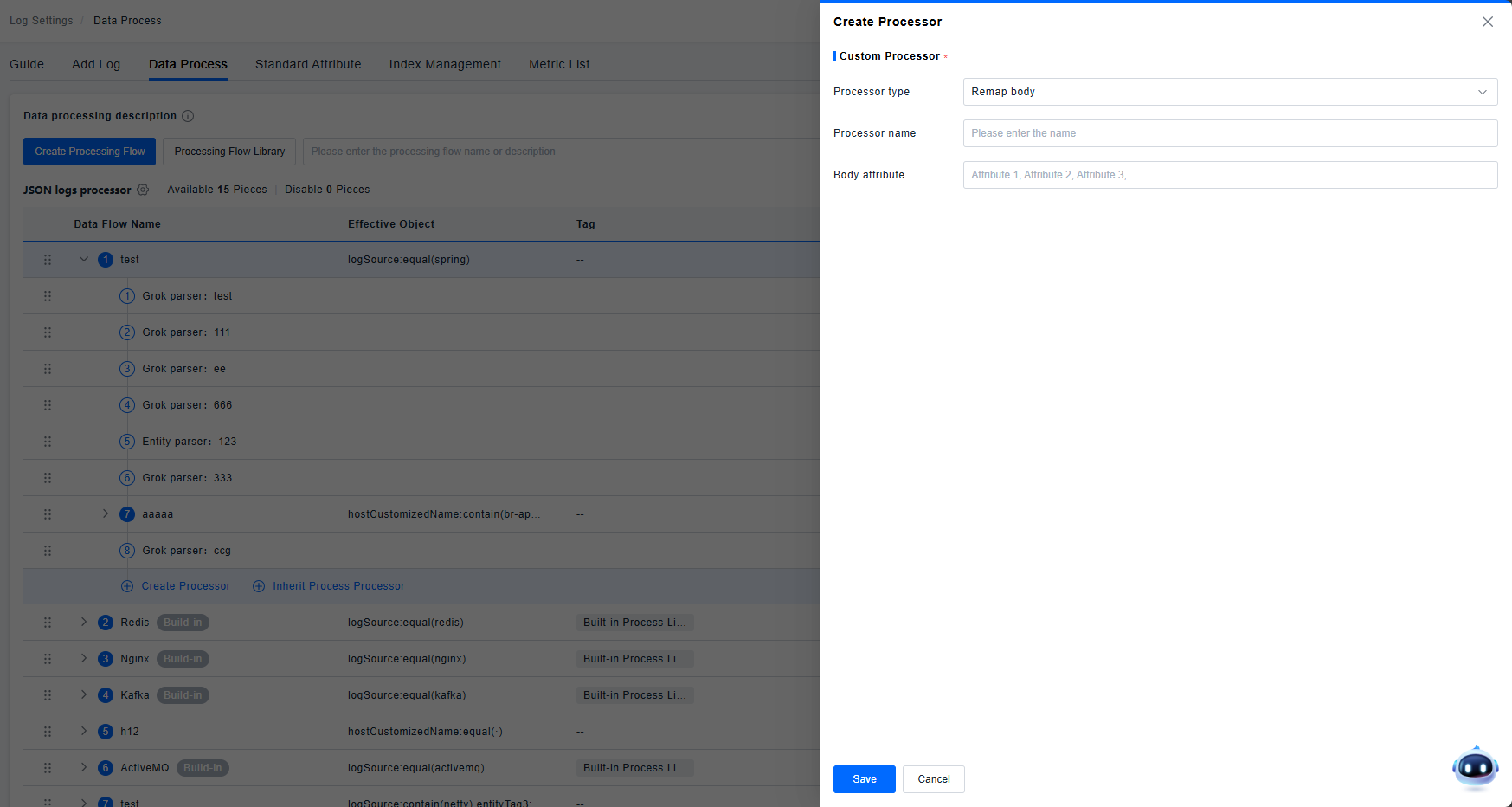
Body Remapper
Maps a specified attribute to the Body field.
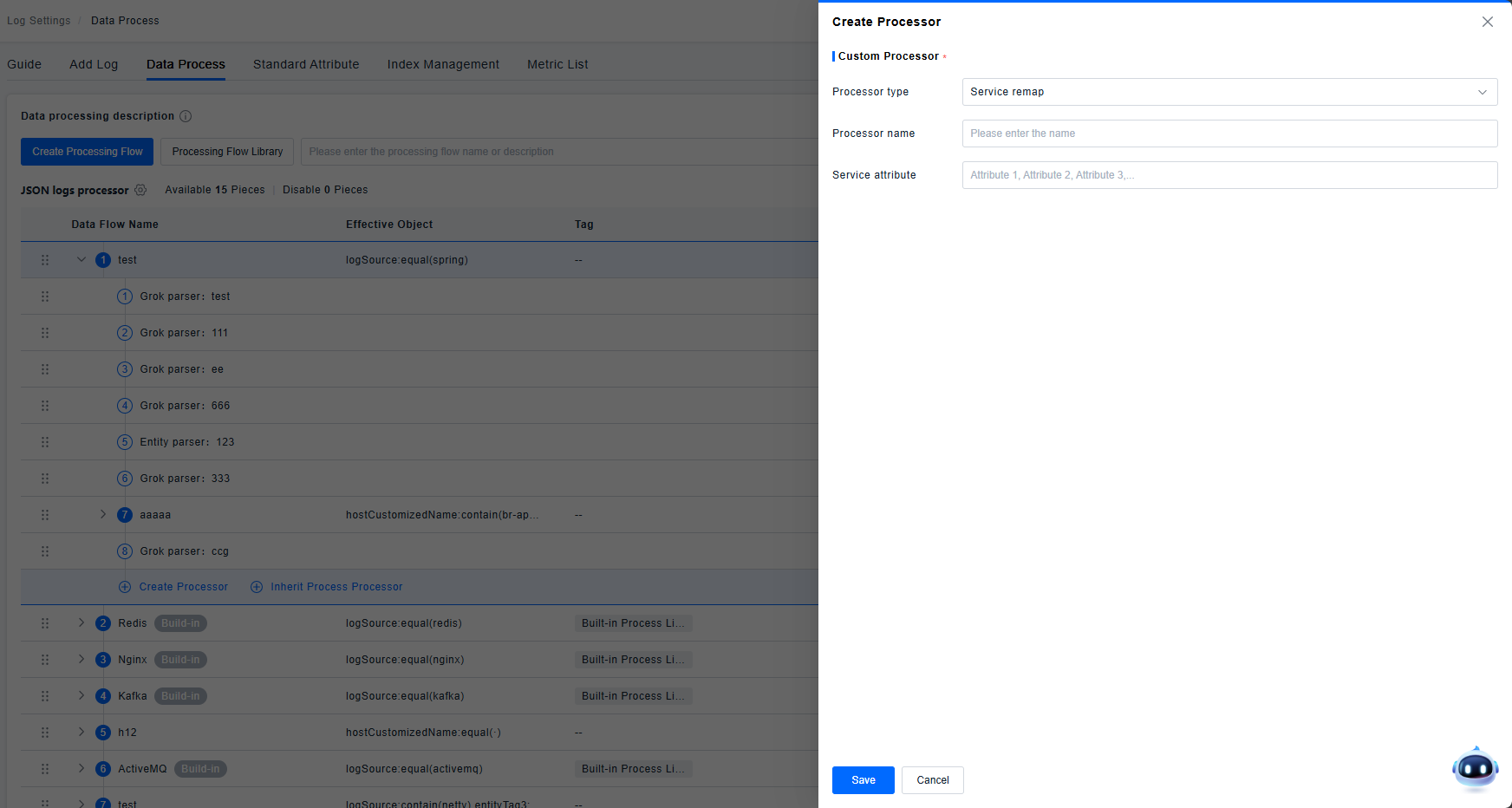
Service Remapper
Maps a specified attribute to the Service field.
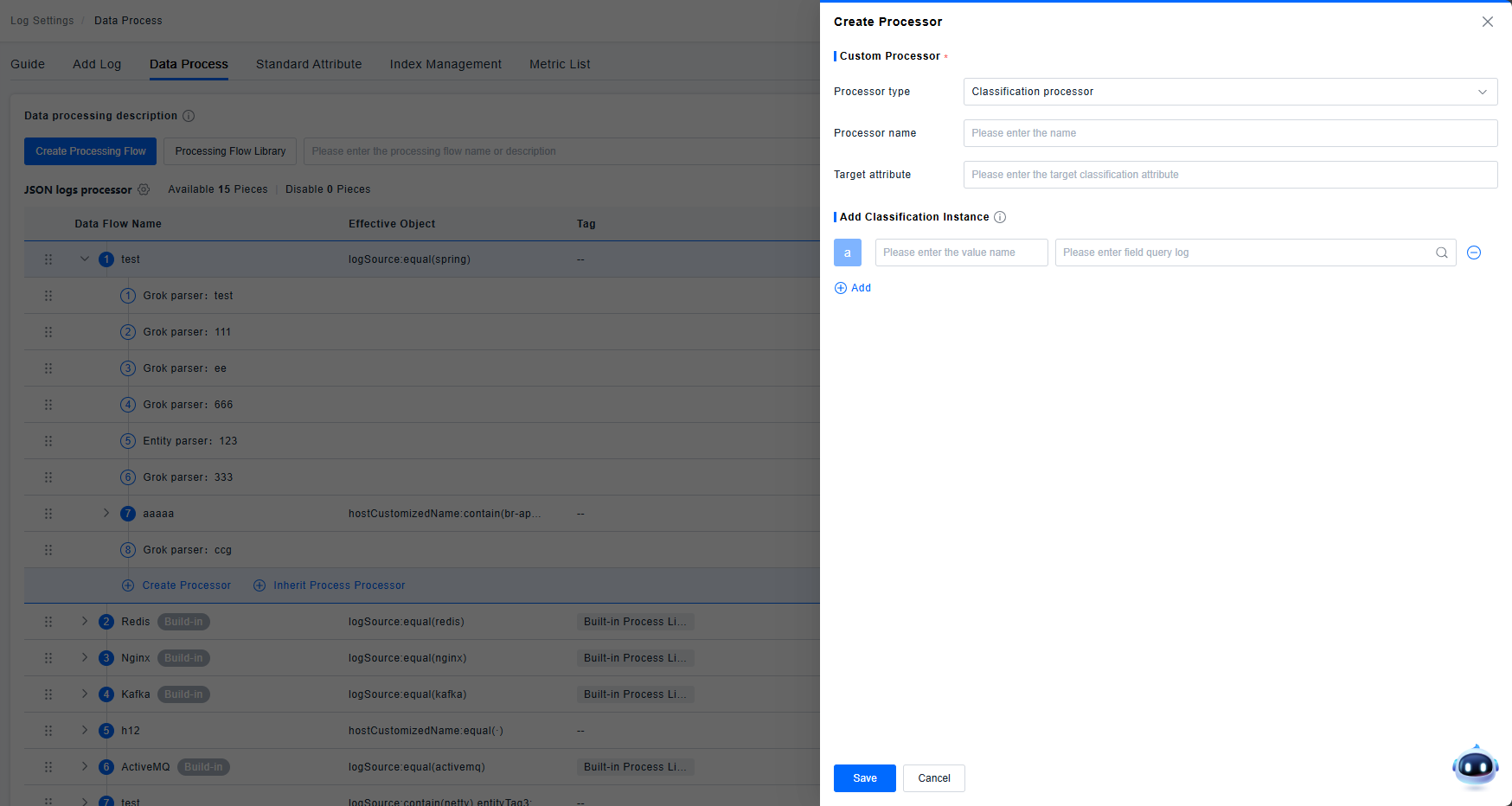
Category Processor
Supports filtering log attributes to generate new categories. Uses input query filters to match objects and maps qualifying logs to a set name. Up to 50 categories can be added. Supports adding, editing, and deleting category items. Clicking a value name reflects the input in the edit box; modifications are synchronized with the added instance.
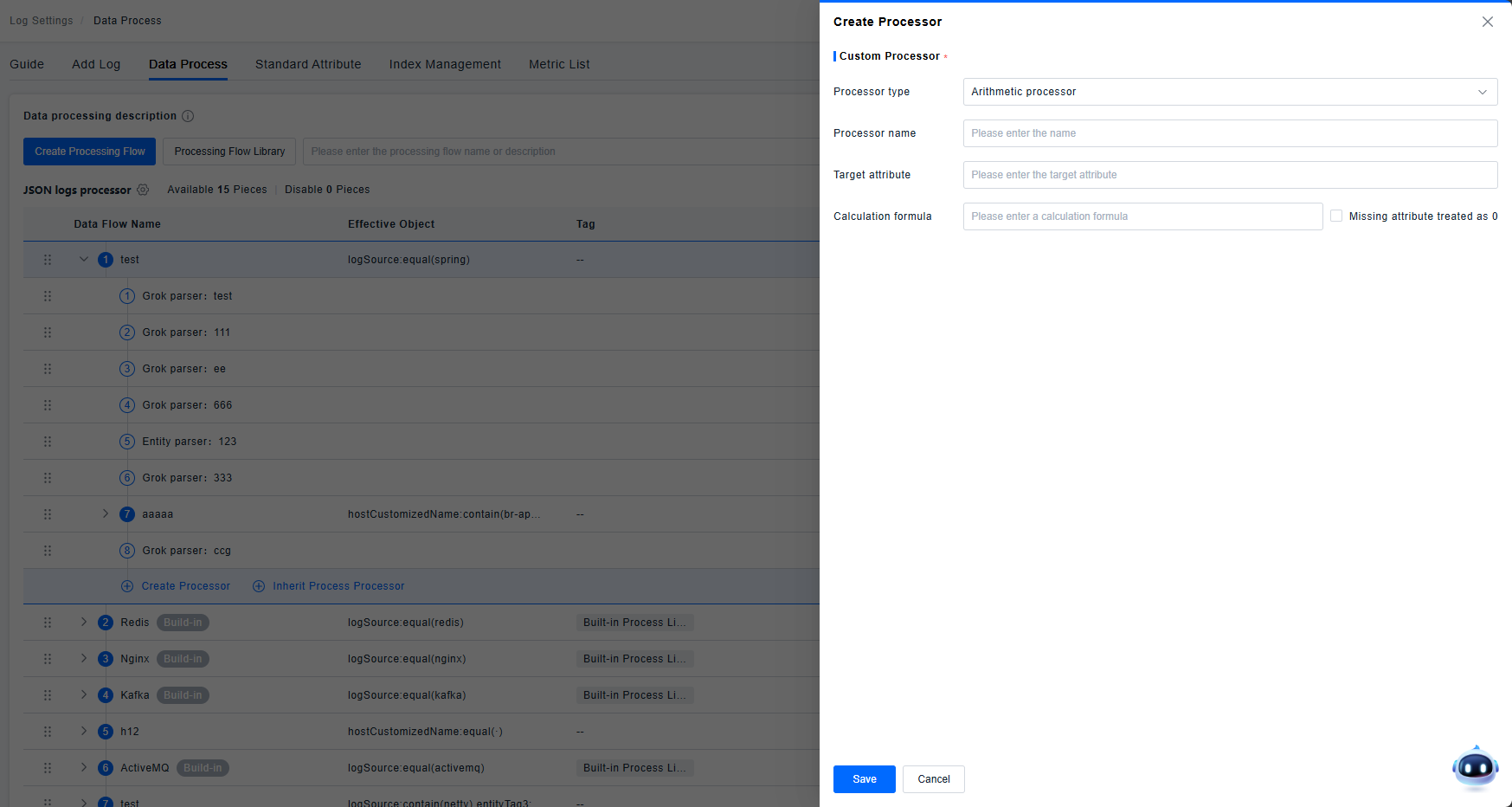
Arithmetic Processor
Supports calculations on attribute values. Allows computation using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, supporting calculations between one or more attributes. Supports configuring missing attributes to be treated as 0.
Supported operators: + - * / ( )
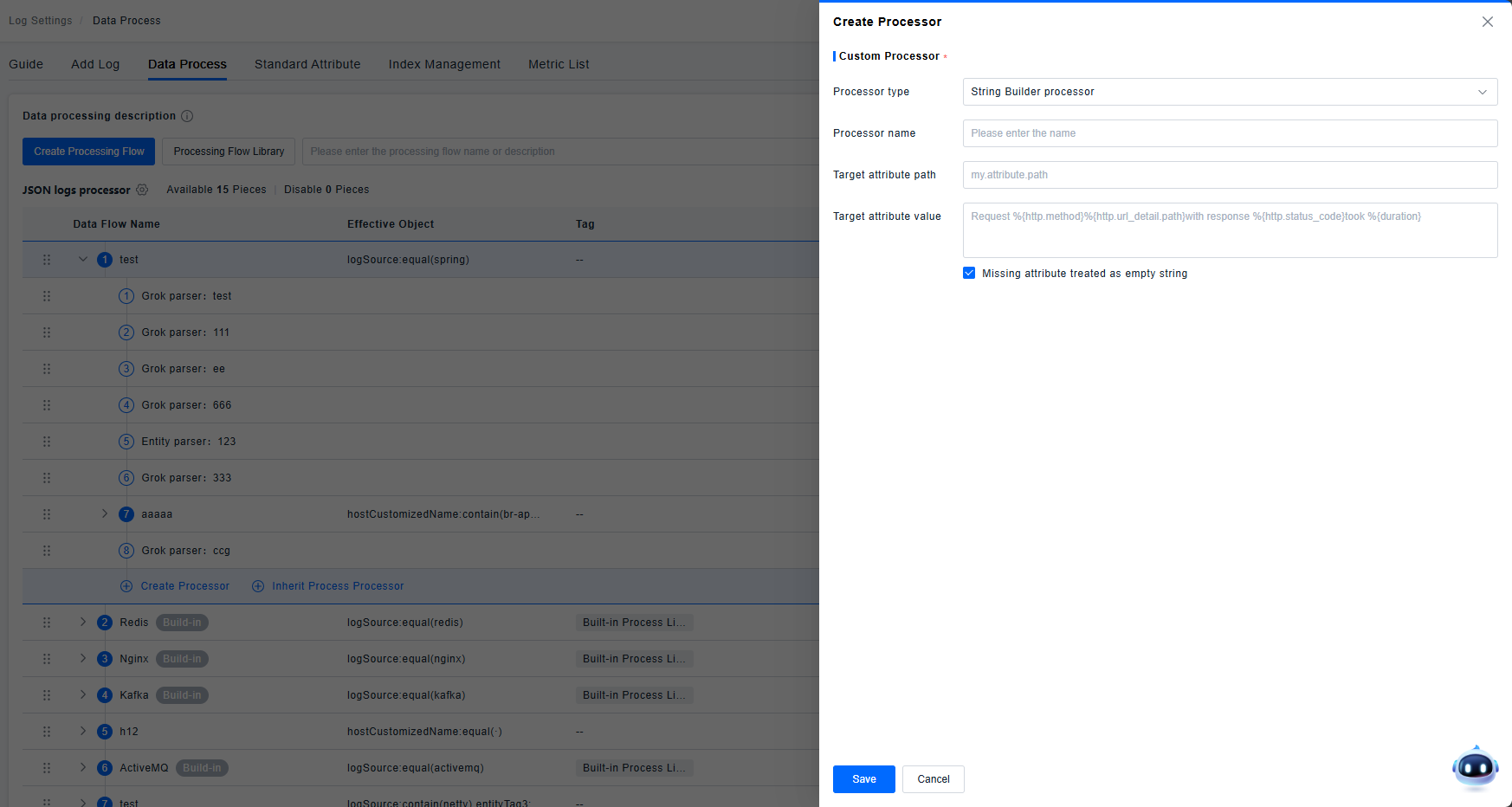
String Builder Processor
Supports combining multiple attributes into a new single attribute. Supports configuring missing attributes to be treated as empty strings.
Trace Id Remapper
Maps a specified attribute to the Trace ID field.
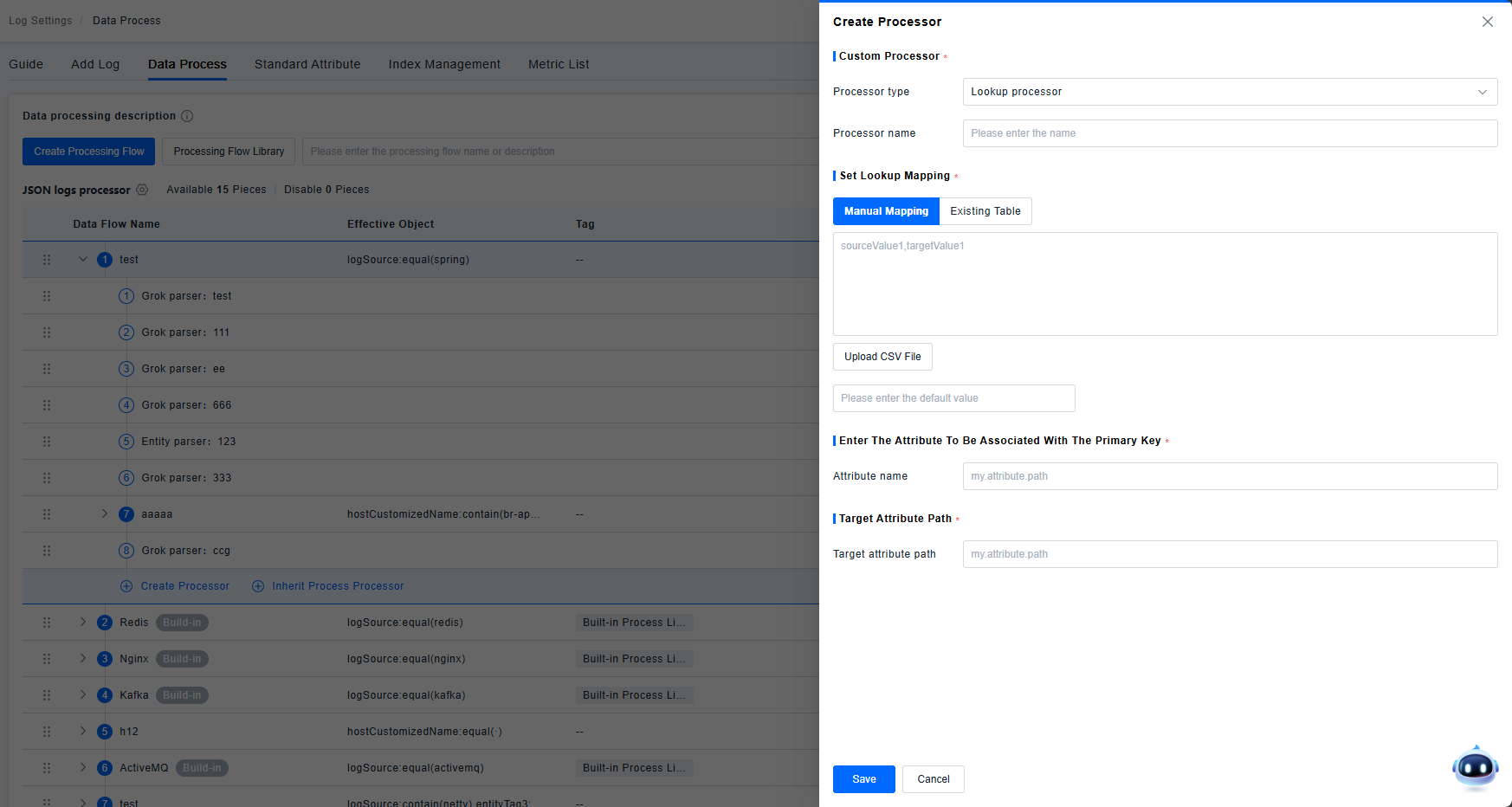
Lookup Processor
Supports enriching log data by associating it with external data.
Supports two methods: manual mapping and table mapping (CSV format supported for tables).
Associates data based on matching primary key values. Supports configuring a Fallback Value: this value is displayed if no matching field value is found.