Index Management
The platform decouples log ingestion from indexing, enabling full-volume log ingestion at a low cost. Indexing can be selectively applied only to logs with analytical value. Indexing strategies can also be adjusted based on business requirements by modifying filters and sampling rates.
Index Management
Index List
Logs are routed to the first index whose filter they match. The priority of indexes can be adjusted.
Index filters allow dynamic control over which logs flow into which index. Indexes support both inclusive filtering and exclusionary filtering.
The platform provides a default main index, which cannot be deleted. It supports editing and log querying.
For user-defined indexes, the platform supports editing, querying logs, and deletion. Deleted indexes remain visible in the list but are marked with a red delete icon. Editing and log querying are still possible for deleted indexes. For exclusion filters, the platform supports editing, querying logs, deletion, and enabling/disabling.
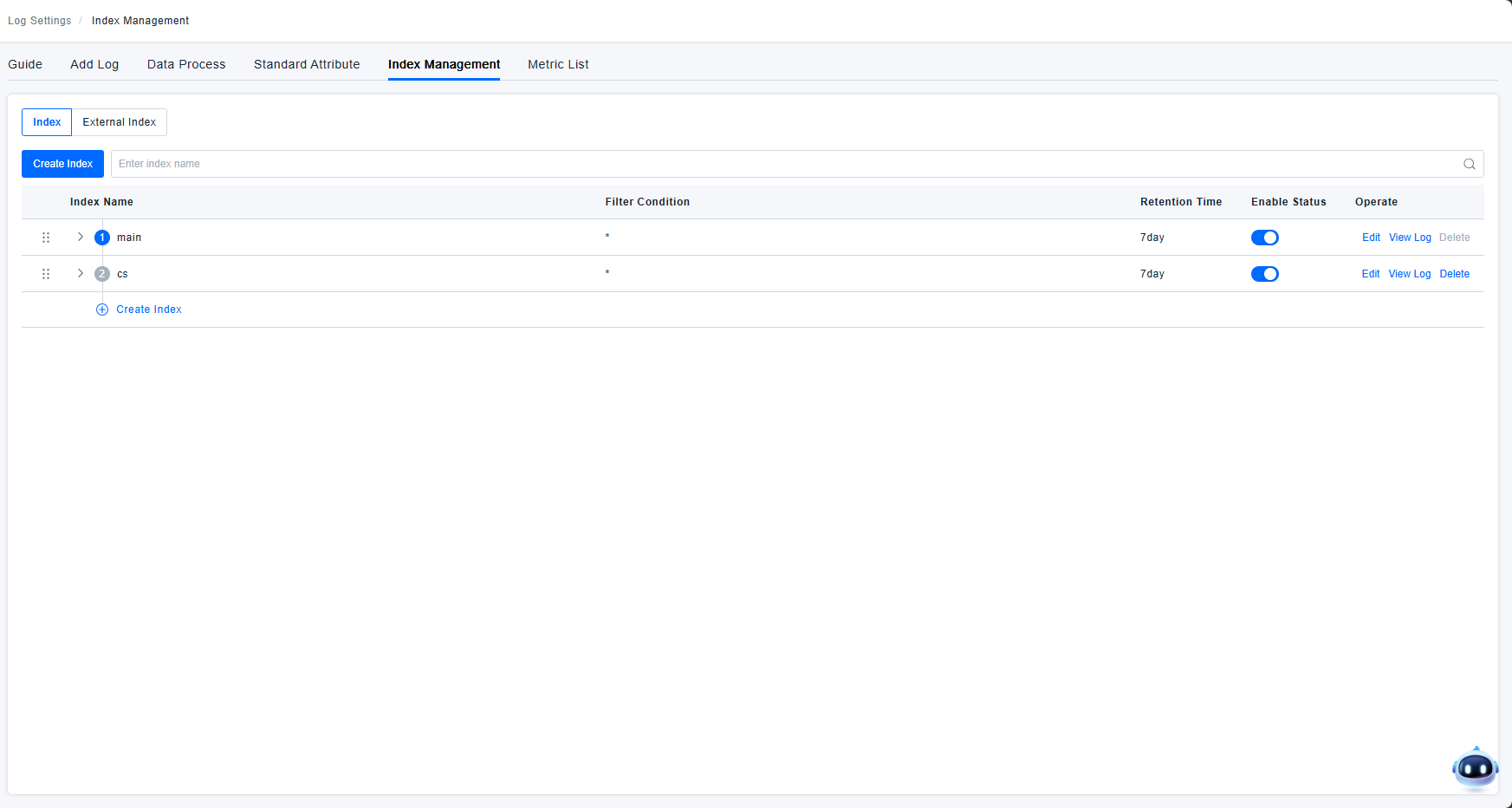
Creating an Index
Log indexes allow you to reorganize data using filtering methods (the same filters as the query component).
You can configure different retention periods (7, 15, 30 days) and quota storage sizes (default 200 million/day, customizable), enabling granular control over your log management budget.
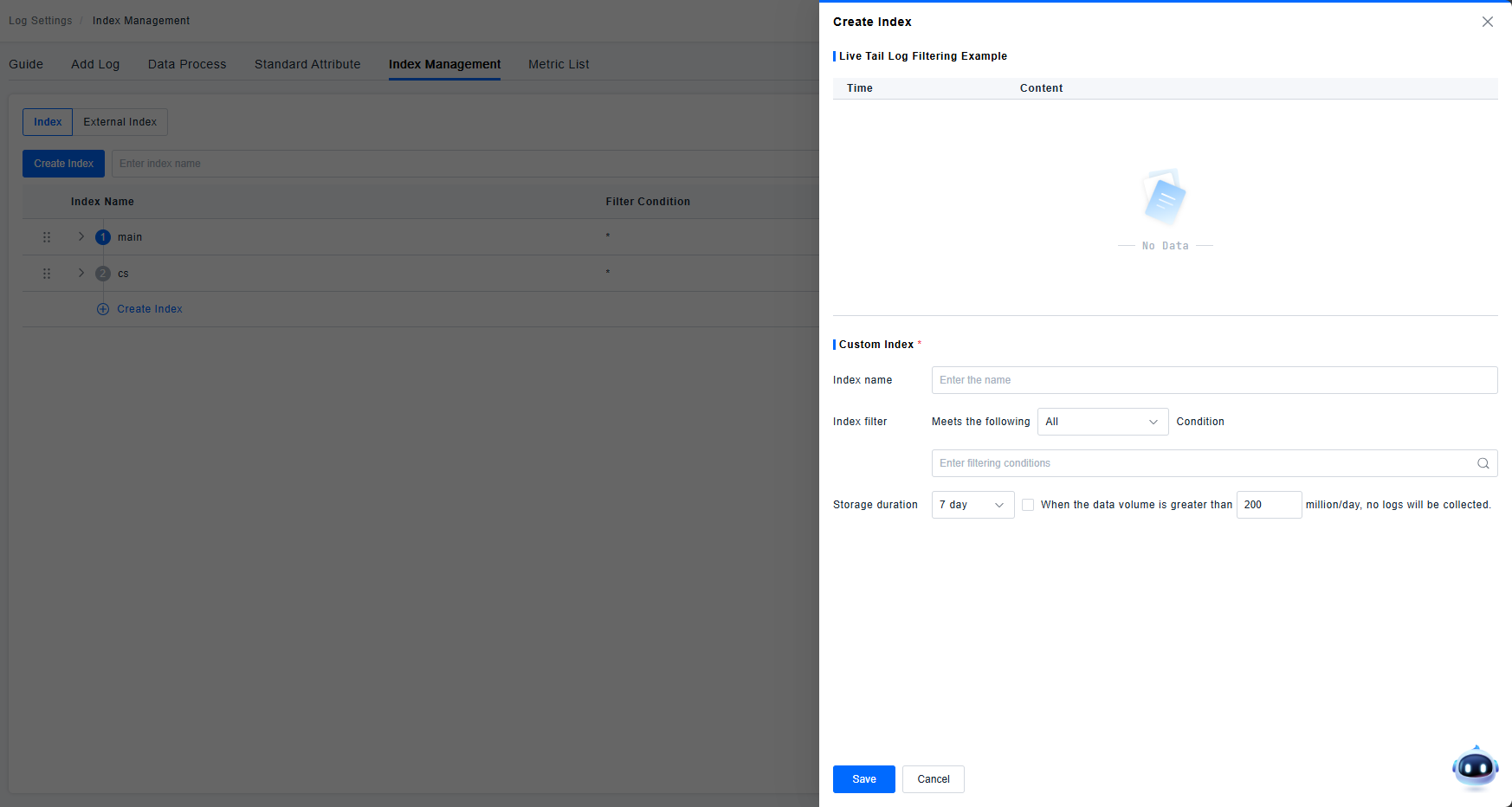
The configuration of exclusion filters is supported, allowing the exclusion of a certain percentage of logs based on attributes, tags, TraceID, or all logs.
External Index
The logging module currently supports two types of external indices: LogEasy and ELK.
LogEasy Index
Integrates with LogEasy data, typically supporting a single log source. When enabled, a "LogEasy" index will be generated in the platform's External Indices section. Click Edit to configure field mappings.
- Context Correlation Field: Specify any field as an identifier for contextual log correlation. During log context analysis, logs with matching values in this field will be recognized as correlated contextual logs.
- Entity Field Mapping:
- Field Association: Map external fields directly to entity fields. For example, when the platform's service identifier is "serviceDetectedName" but the client-side uses "servicename", this mapping ensures queries using the platform's identifier correctly retrieve data. Each entity field can only be mapped once.
- Constant Association: For cases where field association isn't applicable (e.g., Service A uses "sname" instead of the standard "servicename"), set fixed constant conditions. When querying Service A logs, the system will use the configured condition "sname==A".
ELK Index
For ELK integration supporting multiple log indices. After enabling ELK index configuration, the External Indices section supports add, edit, and delete operations.
- Index Name: Custom names must exactly match the index names in the client's ELK environment. Selecting an index will directly query data from the corresponding client-side index.
- Field Mapping: Correlates the platform's log metadata fields with client-side ELK fields.
- Metadata: Selected from log metadata options. The logMessage field is mandatory and cannot be removed.
- ELK Field: The corresponding field key in ELK for each metadata element. Enter the correct field names to establish mapping. When executing conditional queries in the logging module, these will be translated into corresponding ELK field queries against client-side log data.