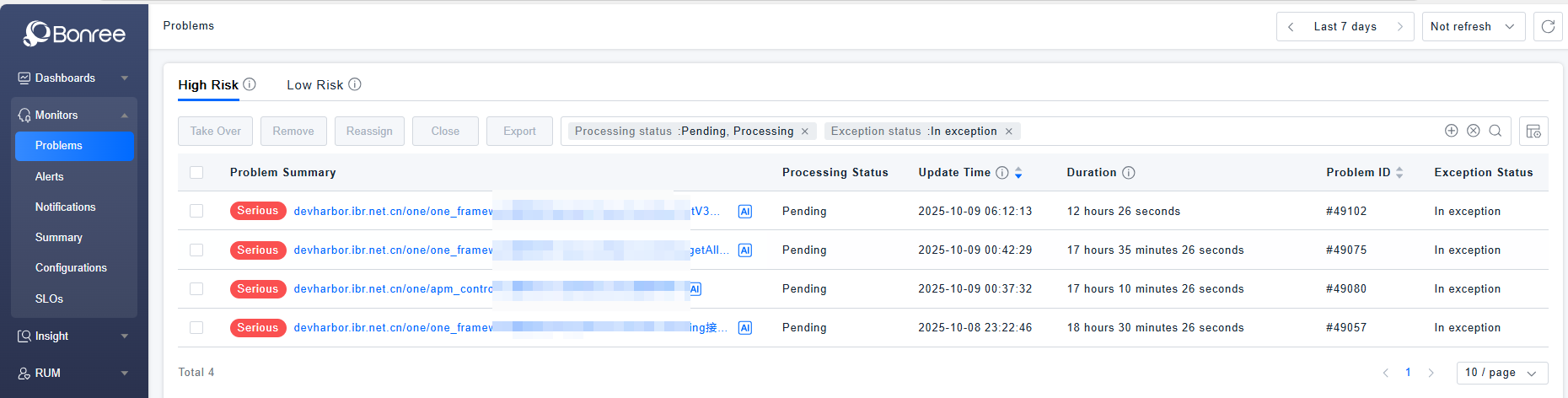
Problems
Prerequisites
Feature Menu Access: Availability of the alerts feature menu. Operation Permissions: read-write, and read-only permissions for alerts. Data Permissions: Access to at least one resource domain within an environment.
Overview
- The Problem List serves as the core information hub of the emergency response system, enabling intelligent aggregation and visual governance of alert data. Through predefined convergence strategies, it automatically clusters discrete multi-source alerts into business-meaningful problem units, forming a unified management view oriented toward impact analysis.
- The list clearly presents key attributes such as problem summary, handling status, severity level, and duration in a structured manner, and deeply integrates the following core elements in the details: associated entity topology (e.g., service/interface dependencies), traceability evidence chains (original alerts and event details), intelligent analysis results (root cause localization and problem replay), and handling process tracing (full lifecycle handling records).
- This multi-dimensional information integration constructs an end-to-end work platform for the operations team, from situational awareness and root cause diagnosis to collaborative handling, effectively improving the efficiency of emergency response to major failures.
Value
- Situational Aggregation and Cognitive Noise Reduction By converging fragmented alerts into business-semantic problems, redundant noise is filtered out, enabling the team to quickly focus on core failures that truly impact business continuity and enhancing emergency decision-making efficiency.
- Root Cause Localization and Impact Analysis The integrated problem replay and root cause analysis functions, combined with associated entity topology, help the team quickly construct fault propagation chains, accurately locate the source of anomalies, and assess the scope of business impact.
- Process Closure and Knowledge Retention Complete handling records ensure full traceability of the problem process from discovery, analysis, and handling to review, promoting the standardization of operational processes while accumulating typical fault patterns and handling solutions for the knowledge base.
Use Cases
-
Daily Operations Monitoring
On-duty engineers use the problem list to monitor system health in real time, quickly claiming and assigning newly generated problems based on status filters.
-
Fault Emergency Response
Upon receiving fault notifications, the team uses the problem list to quickly locate related problems, leveraging root cause analysis and entity topology for impact assessment and emergency decision-making.
-
Fault Retrospective Analysis
The operations team reviews historical problem records and complete processing logs to analyze the fault response timeline and handling effectiveness, optimizing convergence strategies and emergency procedures.
-
System Health Assessment
By analyzing the frequency, duration, and resolution efficiency of problems in specific services/modules, system stability is evaluated to guide capacity planning and architectural optimization.
Operational Scenario
- Query: When users need to search for target problems in the problem list, they can query based on problem fields and entity attributes in the search box. The filter component also supports recording recently used filters and provides quick filter condition template management.
- Close: When users need to close some pending or in-progress problems, they can batch select problems and click the 【Close】 button to perform the operation.
- Export: When users need to export data from the problem list locally, they can batch select problems and click the 【Export】 button. Each export generates a single CSV file, with a maximum of 100 problem records supported per export.
- Time Frame Selection: Click the time frame selector in the upper right corner to quickly select or customize a time range. It also supports selecting recently used time periods.
- Take Over: When a problem is in pending status, users need to click "Take Over" to change it to in-progress status, indicating that someone is currently handling it.
- Remove: When a problem appears in the high-risk list but doesn't require special attention, users can click the "Remove" button to move the problem from the high-risk list to the low-risk list.
- Reassign: When a problem is in progress but the current user cannot continue handling it, they can reassign it to another person for resolution.
Get Started
Problems List
- Log in to Bonree ONE.
- Navigate to Intelligent Alerting > Problems.
- Supports alert querying, closing, exporting,take over, remove,reassign.
- The list supports customizable headers, provides default display fields, and allows defining display columns according to usage scenarios.
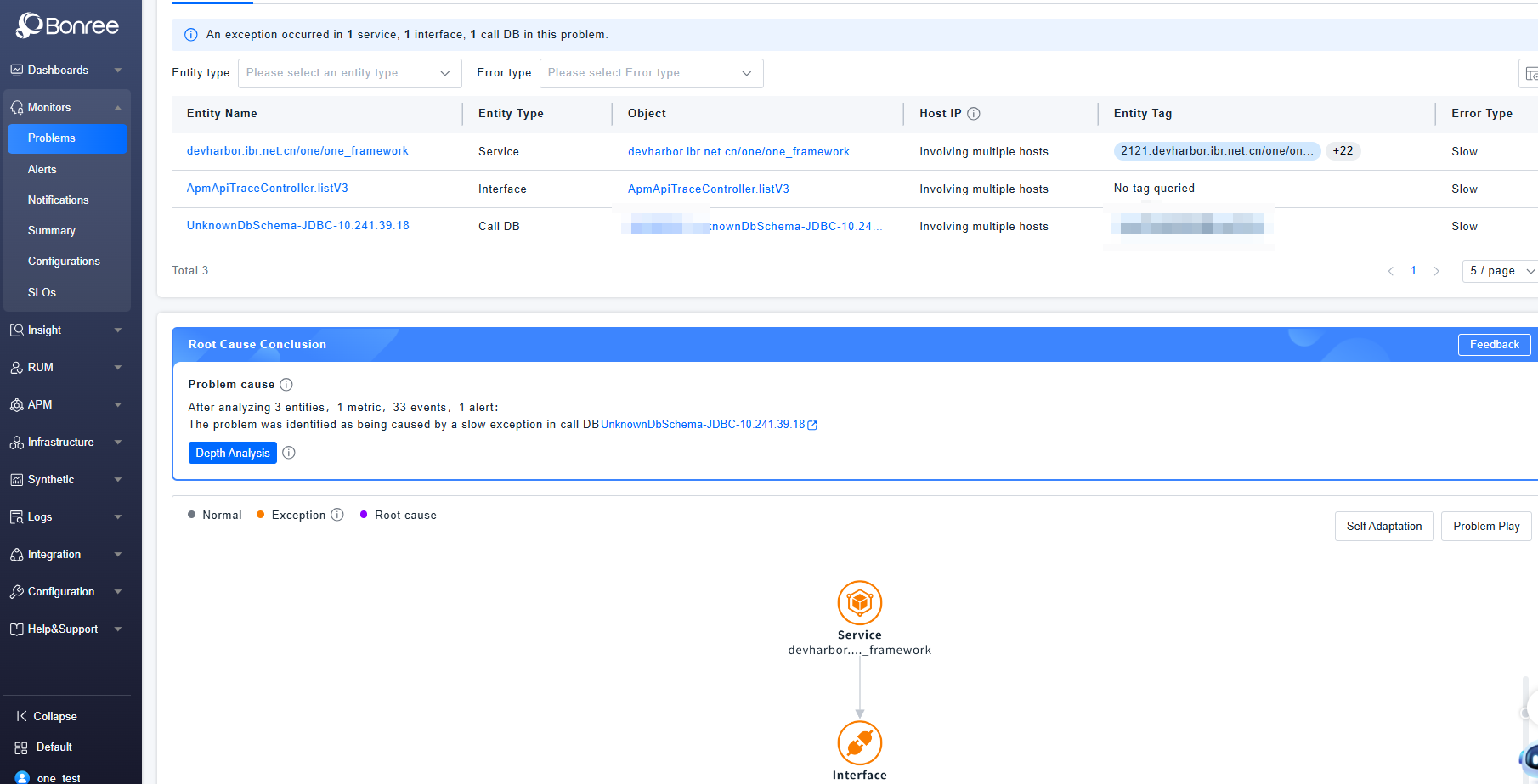
Problems Details
-
Clicking on any row of a problem will navigate to the details page of the corresponding problem.
-
The problem details include three sections: Basic Information, Root Cause Analysis, and Handling Records.
-
Basic Information includes three tabs: Entity List, Alert List, and Timeline Chart, which display the list of all abnormal entities in the problem, all alert details, and the change graph of alert status levels, respectively.
-
Root Cause Analysis refers to the process of locating the deepest possible cause after algorithmically converging abnormal alert entities. It provides a converged root cause topology graph and problem replay to help trace the problem evolution process and quickly locate and resolve abnormalities. Root cause problems are only generated after the AI Root Cause Convergence strategy is enabled.
-
Handling Records display the complete history from problem generation, notification triggering, suppression, to status changes, until the problem is closed.