Interface Identification
ONE supports interface identification according to rules. Interface identification rules are used to precisely define the identification logic of interfaces in the system. They support identifying interfaces through custom rules or default rules, and can configure interface entrances and request attributes to meet the needs of refined management and monitoring of interfaces in different business scenarios.
Custom Interface Identification Rules
Creating Custom Interface Identification Rules
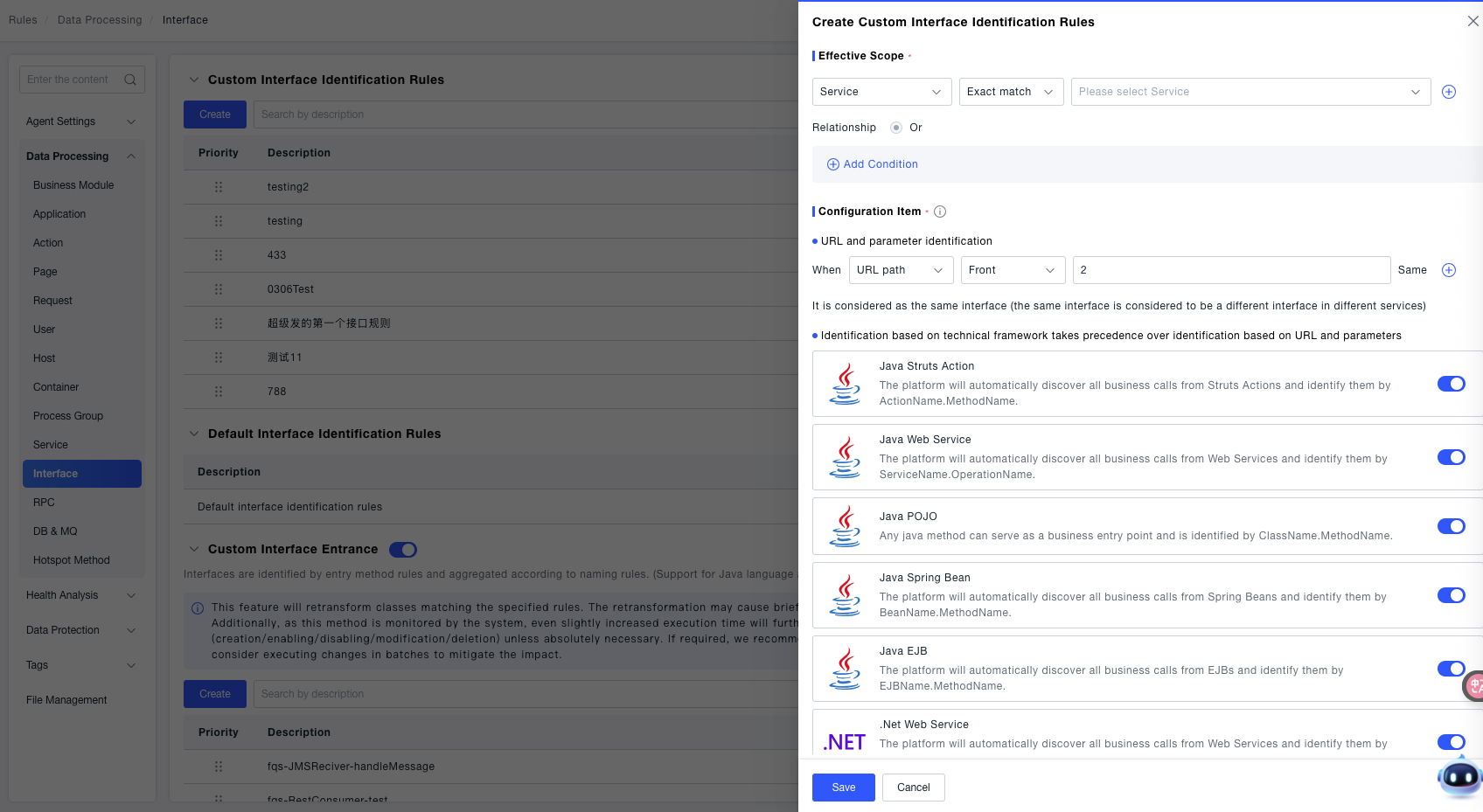
Effective Scope Configuration: Select a service as the effective dimension, choose "exact match" as the matching method, and select a specific service from the drop-down box (the rule only takes effect for the interfaces of the selected service).
Configuration Items:
Two methods are supported for identifying interfaces: URL and parameters, and technical framework.
In URL and parameter identification, the priority is: Request method > Request parameters > Header > Cookie > Session.
The generated format is " GET: url ? Request parameter = xx & Header = yy & Cookie = zz & Session = xx ".
Two methods are supported for identifying interfaces:
- In URL and parameter identification, the priority is: Request method > Request parameters > Header > Cookie > Session, and the generated format is " GET: url ? Request parameter = xx & Header = yy & Cookie = zz & Session = xx ". In URL and parameter identification, set the matching rule for the URL path (for example, select "URL path", choose "prefix" as the matching method, and enter the path value
/api) to identify interfaces with specific paths. - Technical Framework Identification Configuration: Provide identification switches for various technical frameworks (such as Java Struts Action, Java Web Service, Java POJO, Spring Bean, .NET Web Service, etc.). Turn on the corresponding switches according to the technical framework actually used by the application, and the platform will automatically identify business calls under the framework and complete interface identification.
Request Attribute Identification Configuration: It has higher priority than "Technical Framework Identification" and "URL Identification" (only effective when Java-type frameworks are in effect). You can check "Re-identify name (if not checked, append request attributes after the identification field)" to further refine the attribute basis for interface identification.
Rule List
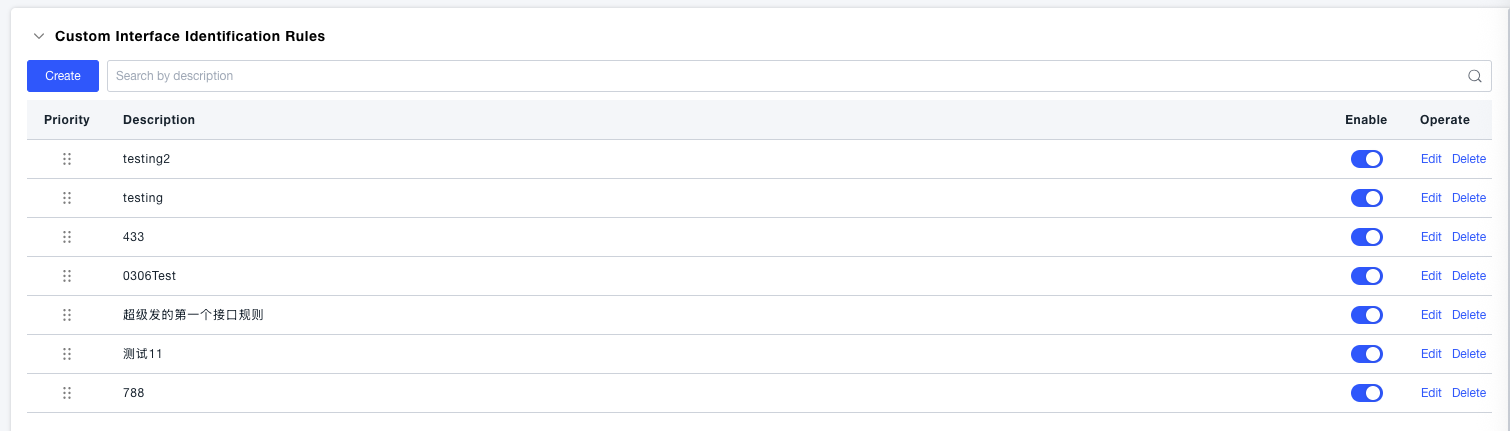
After successful creation, the created custom rules are displayed, including priority, description, enabled status (controlled by a switch), and operations (edit, delete).
Default Interface Identification Rules
Display system-preset general interface identification rules, and provide editing operations to adjust the default rules to adapt to general scenarios.

Custom Interface Entry
Click the create button in the custom interface entry area and configure according to the following steps:

Effective Scope Configuration: Support scope matching configuration by services, service tags, process groups, and process group tags.
Configuration Items:
It is used to accurately match the interface entry of specific classes and methods. In the Matching Class Rules module, you can set:
Matching Class: Select the class name, choose the matching method (such as equal to), and enter the target class name;
Matching Method: Select the method name, choose the matching method (such as equal to), and enter the target method name;
Naming Rule Configuration:
Custom interface name: Manually enter a custom entry name;
Or check to use class name for naming, use method name or method value for naming to quickly generate the interface entry name.
Description: Fill in the purpose of the rule in the input box for easy subsequent identification and management.
Rule List
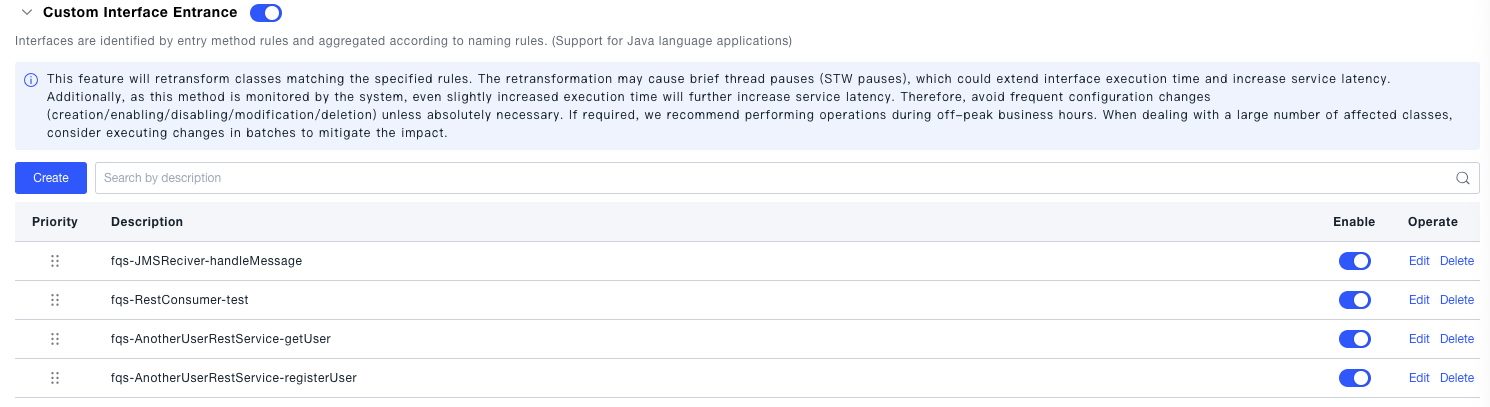
After successful creation, the successfully created rules are displayed, including priority, description, enabled status (controlled by a switch), and operations (edit, delete).