Introducing the role concept of ONE
The ONE platform builds its access control capabilities based on the RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) concept, implementing batch permission management for administrators through a three-layer mapping of User --> Role --> Permission.
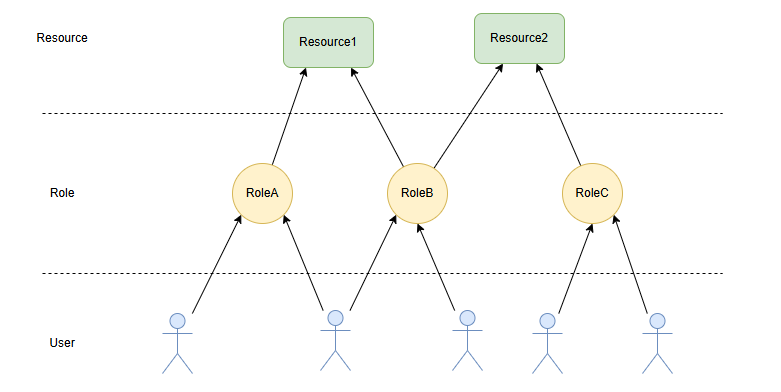
In the ONE platform, a Role essentially represents a collection of permissions that users should possess when accessing the platform. Therefore, during the permission system planning phase, administrators need to abstract different types of personnel into different roles based on the expected functionalities and permission differences when they use the ONE platform within the organization.
Simple Example of Role Definition
According to actual division of responsibilities, operations personnel within the organization need to perform tasks like probe installation and rule configuration in the ONE platform, while developers only need to use the data collected by probes to analyze problems on the platform.
Based on the characteristics of the above scenario, platform users can be abstracted into two roles: "Operations" and "Developer". Subsequently, create these two roles in the ONE platform's Role Management function and define the permission content for each role based on the expected functional and operational permissions. After associating the roles with personnel, functional permission control for operations personnel and developers can be achieved.
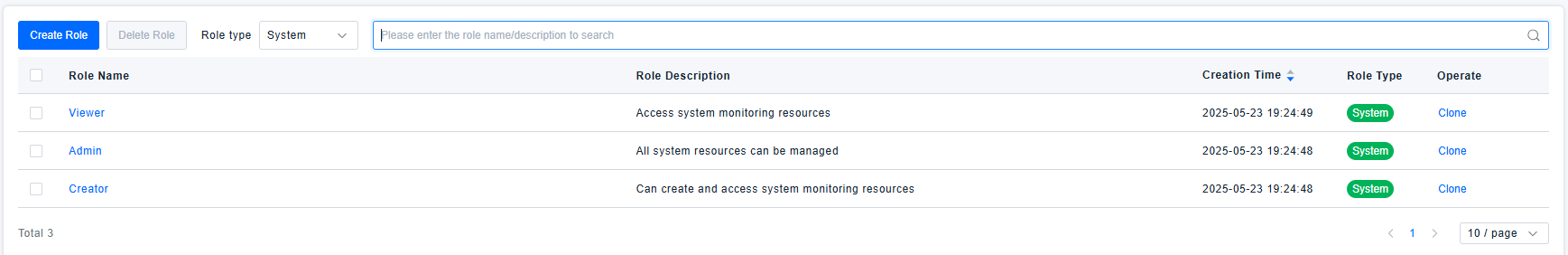
To facilitate user adoption, the platform comes pre-configured with three roles: Viewer, Creator, and Admin, representing read-only permission users, read/write permission users, and administrators respectively. If customers do not have strict permission control requirements for ONE platform usage, they can use these pre-configured roles to achieve simple user permission control.
RBAC Model Explanation
RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) is an access control mechanism that manages system access by defining the relationships between roles, permissions, and users. In the RBAC model, permissions are assigned to roles rather than directly to users. Users obtain corresponding permissions by being assigned to one or more roles. This model simplifies permission management, especially in large organizations. When user roles change, it only requires adjusting the user's role assignments without needing to reconfigure each permission individually.