Slow Identification
Slow Identification is used to configure thresholds for slow performance detection. When a specific metric reaches the configured threshold, it is considered slow and indicative of impacted user experience.
Application Startup
The application list here includes all App applications and Mini Program applications. Select an application to configure its slow startup threshold on the current page.
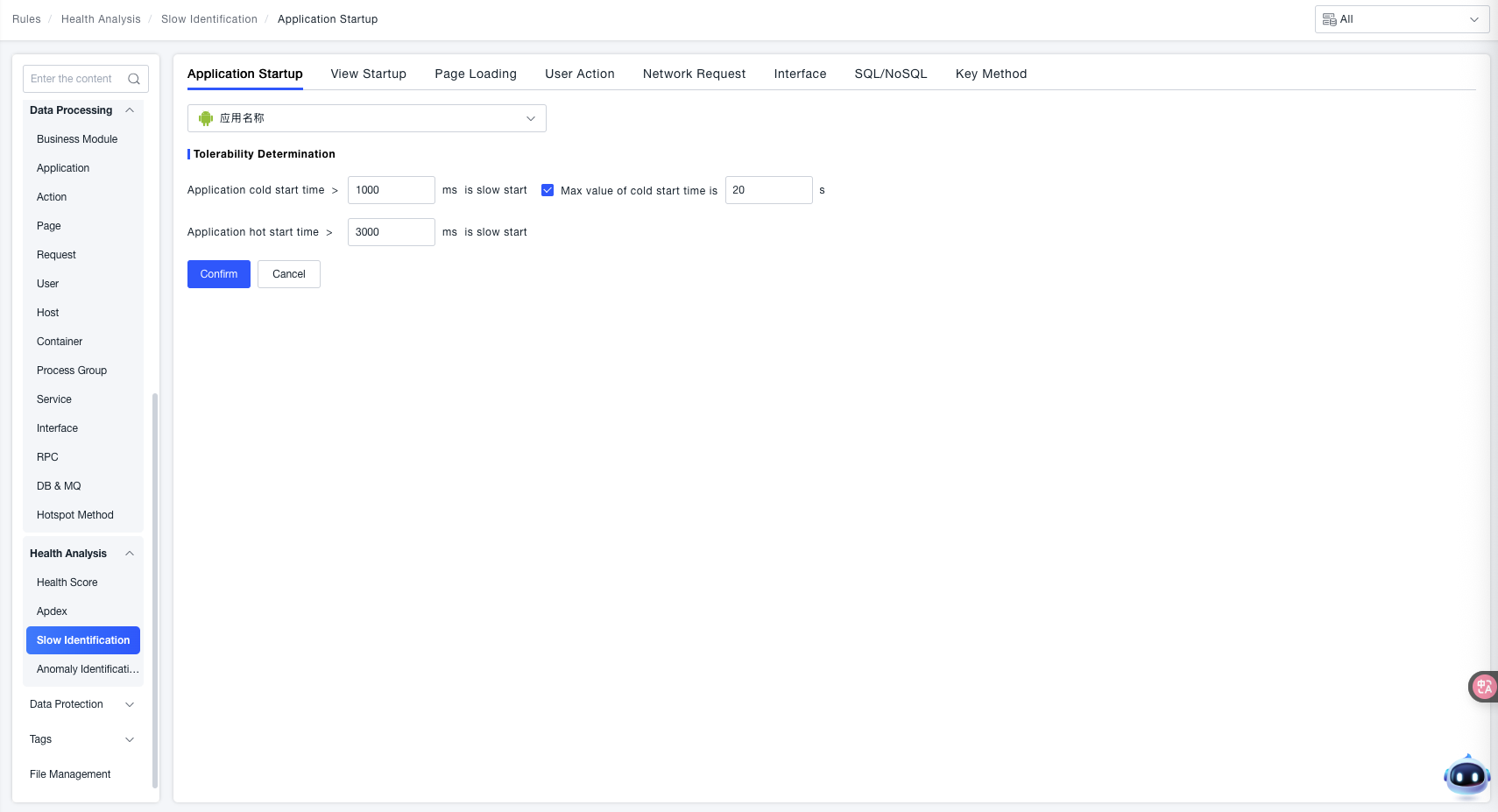
Cold Startup Identification:
- When the "Application Cold Startup Duration" exceeds the set threshold (e.g.,
1000 msin the example), it is identified as a "Slow Startup". - Supports checking the "Cold Startup Time Upper Limit" and setting a duration (e.g.,
20 sin the example) to restrict the maximum tolerable time for a cold startup.
Warm Startup Identification: When the "Application Warm Startup Duration" exceeds the set threshold (e.g., 3000 ms in the example), it is identified as a "Slow Startup".
Feature Value: By customizing the duration thresholds for cold and warm startup, scenarios where the application "starts too slowly" can be accurately identified, providing clear criteria for subsequent startup performance optimization and troubleshooting of abnormal startup issues.
View Startup
The application list here includes all App applications and Mini Program applications. Select an application to configure the slow startup threshold for all views under the current application on this page.
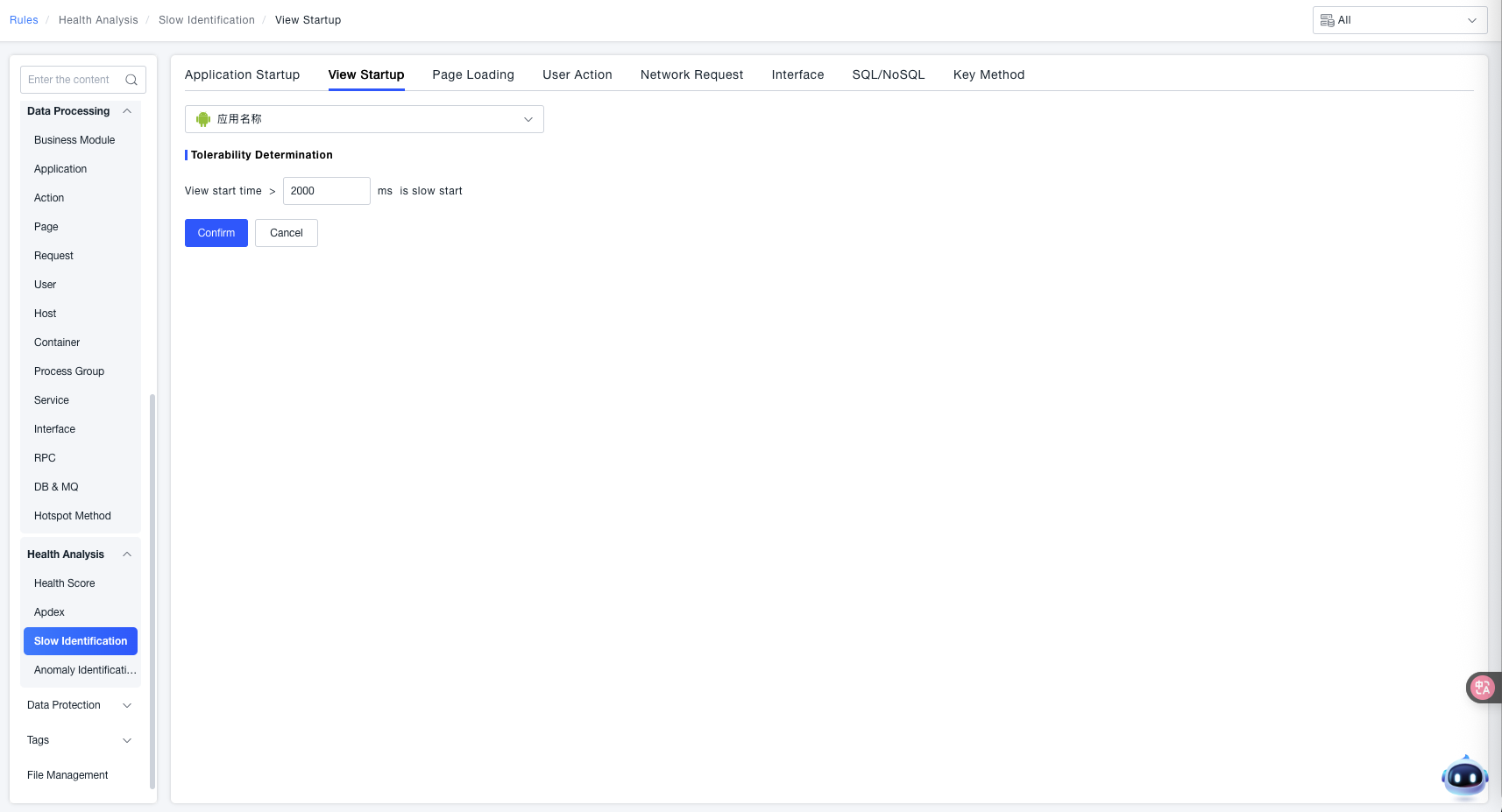
Tolerable Identification: When the "View Startup Duration" exceeds the set threshold (e.g., 2000 ms in the example), it is identified as a "Slow Startup".
Feature Value: By customizing the duration threshold for view startup, scenarios where the application "view starts too slowly" can be accurately identified, providing clear criteria for subsequent view startup performance optimization and troubleshooting of abnormal startup issues.
Page Load
The application list here includes all App applications and Web applications. Select an application to configure the slow load threshold for all pages under the current application on this page.
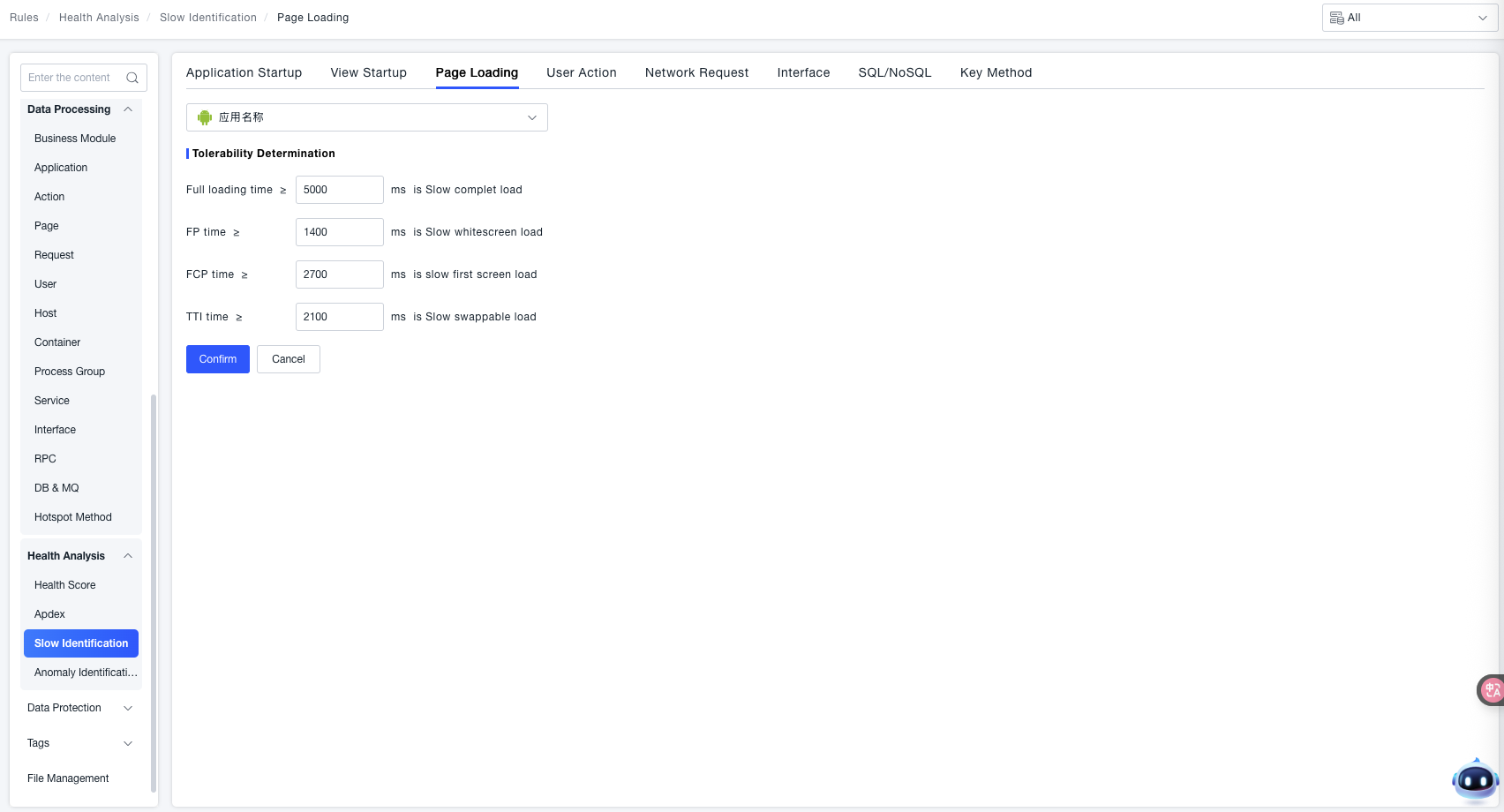
Tolerable Identification: Set corresponding duration thresholds for different stages of page loading. When the duration is greater than or equal to the set value, it is identified as a "Slow Load":
- When Time to Fully Loaded ≥ the set value (e.g.,
5000 msin the example), it is identified as "Slow Fully Loaded". - When FP (First Paint) Duration ≥ the set value (e.g.,
1400 msin the example), it is identified as "Slow White Screen Load". - When FCP (First Contentful Paint) Duration ≥ the set value (e.g.,
2700 msin the example), it is identified as "Slow First Screen Load". - When TTI (Time to Interactive) Duration ≥ the set value (e.g.,
2100 msin the example), it is identified as "Slow Interactive Load".
Feature Value: By customizing duration thresholds for different key stages of page loading (Fully Loaded, White Screen, First Screen, Interactive), scenarios where the application "page loads too slowly" can be accurately identified, providing clear criteria for subsequent page load performance optimization and troubleshooting of abnormal load issues.
User Actions
Slow Action
The ONE platform allows users to manage the identification of anomalous actions. Users can make anomaly identification meet expectations by using custom rules or modifying default rules.
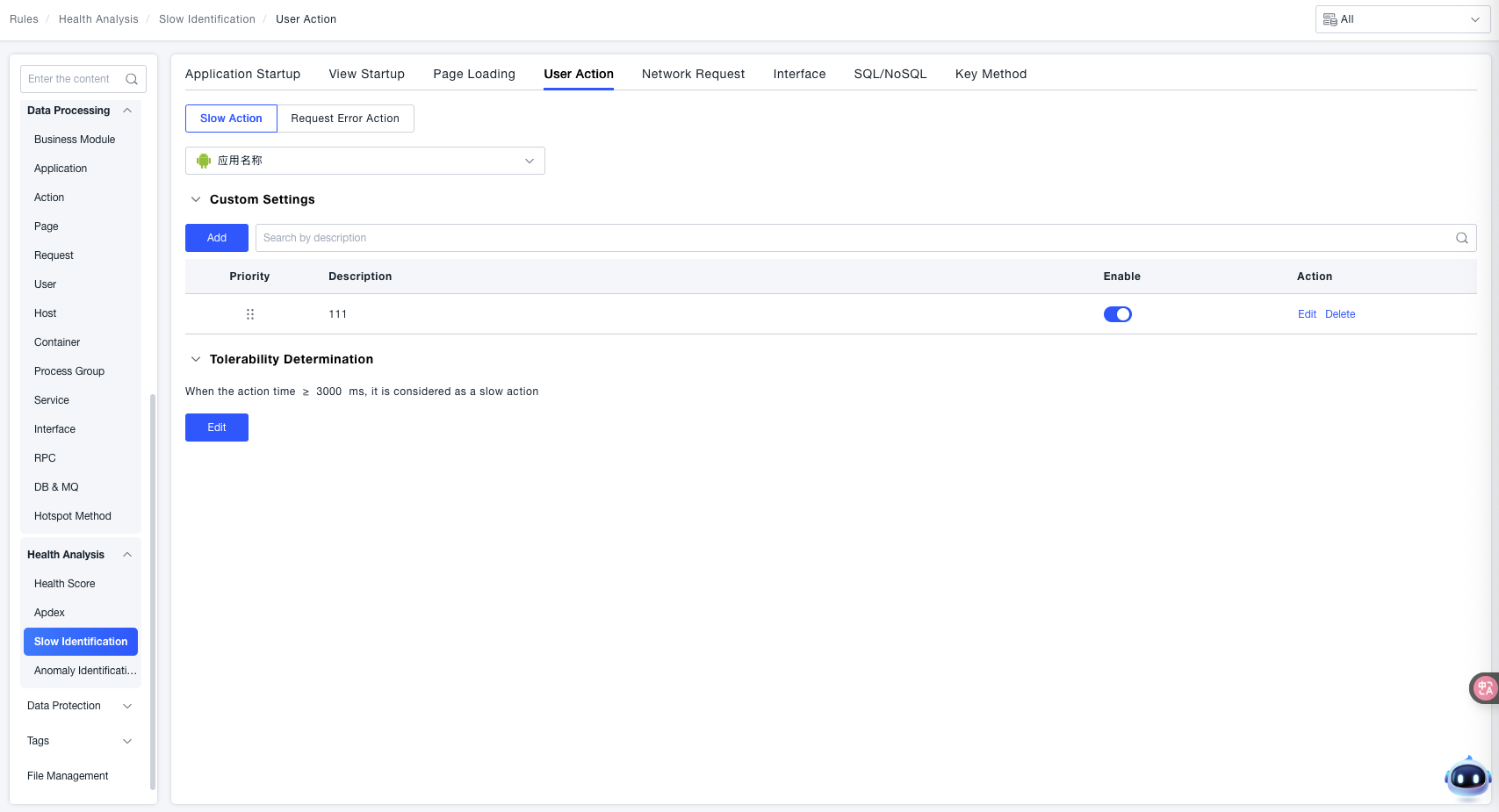
Custom Settings:
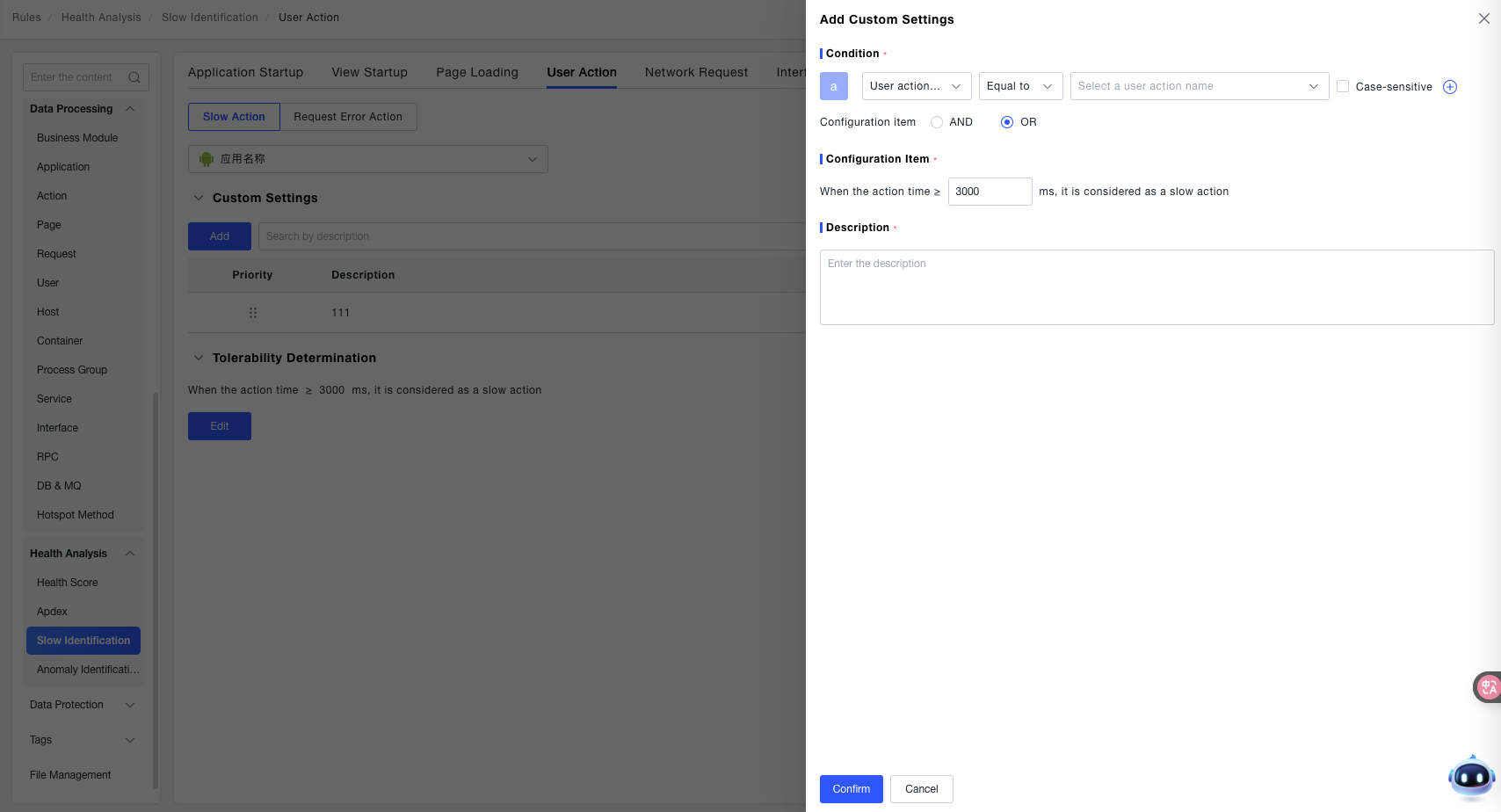
Click Add to create a custom rule:
- Condition: Used to specify the scope of user actions for which the custom rule takes effect.
- Configuration Item: Used to define the duration threshold for identifying a "Slow Action". 'When the action duration ≥ [X] ms, it is considered a slow action' (the threshold is
3000 msin the example). That is, when the duration of the target user action exceeds this threshold, it will be identified as a "Slow Action".
Tolerable Identification (Slow Action Scenario): When the "Action Duration ≥ Set Threshold" (e.g., 3000 ms in the example), it is identified as a "Slow Action".
By combining custom rules for "User Action Scope + Duration Threshold", "Slow Action" scenarios for specific user actions can be accurately identified, providing more detailed criteria for locating and optimizing performance issues related to user actions.
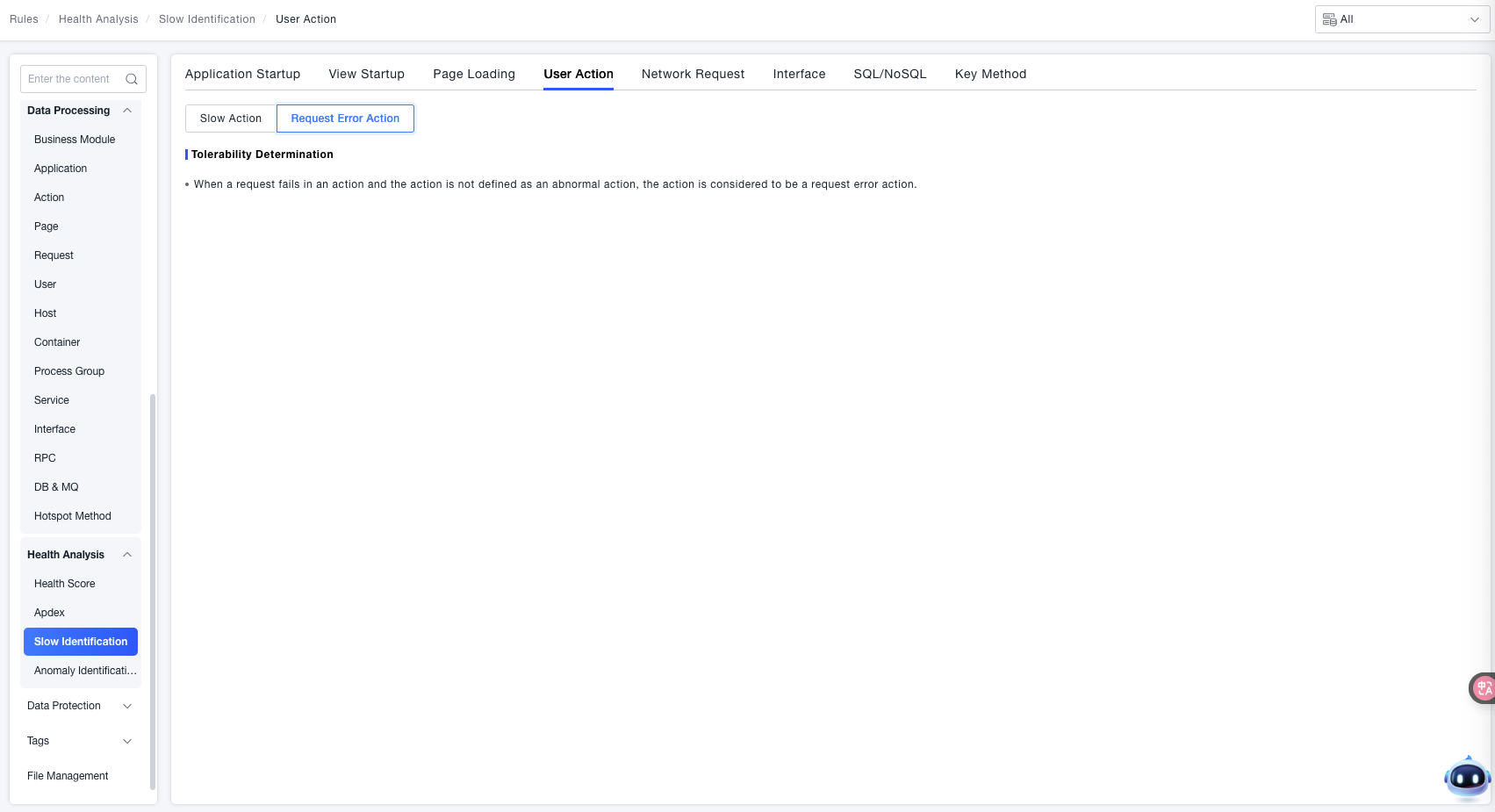
Request Error Action
When a request failure occurs during an action, and that action has not been defined as a Failed Action, the system considers the action a Request Error Action.
Network Requests
Slow network request detection is divided into "Default Settings" and "Custom Settings". The priority of "Custom Settings" is higher than "Default Settings". Multiple "Custom Settings" can be configured, and the order of effectiveness is consistent with their priority.
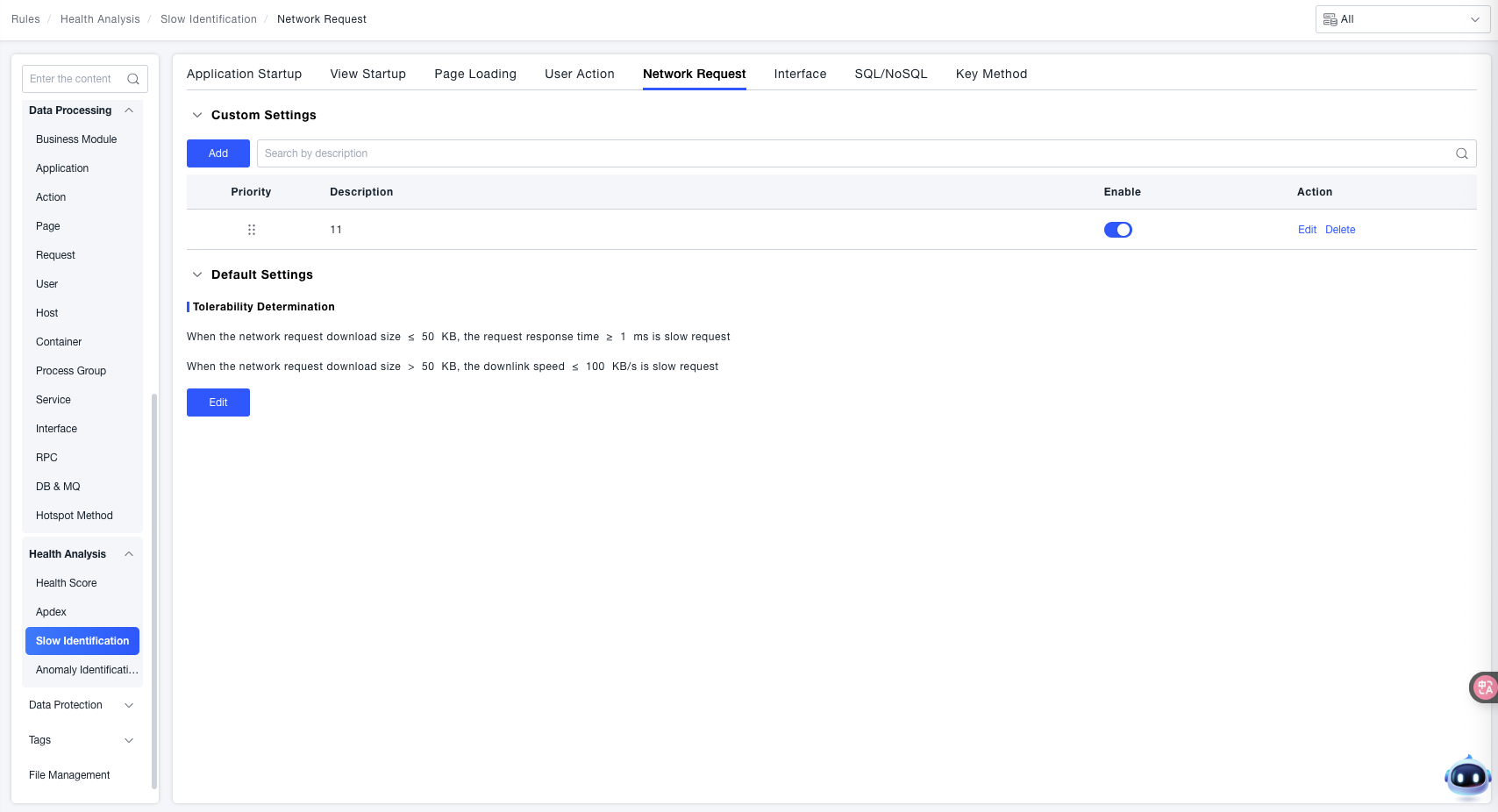
Tolerable Identification
- When the Network Request Download Size ≤ 50 KB, if the "Request Response Time ≥ 1 ms", it is identified as a "Slow Request".
- When the Network Request Download Size > 50 KB, if the "Download Speed ≤ 100 KB/s", it is identified as a "Slow Request".
Through the granular configuration of "Custom Rules" and the global fallback of "Default Rules", network "Slow Request" scenarios under different download scales can be accurately identified. This provides clear criteria for network request performance optimization and troubleshooting of abnormal requests, ensuring the efficiency and stability of application network interactions.
Interfaces
Slow service interface detection is divided into "Default Settings" and "Custom Settings". The priority of "Custom Settings" is higher than "Default Settings". Multiple "Custom Settings" can be configured, and the order of effectiveness is consistent with their priority.
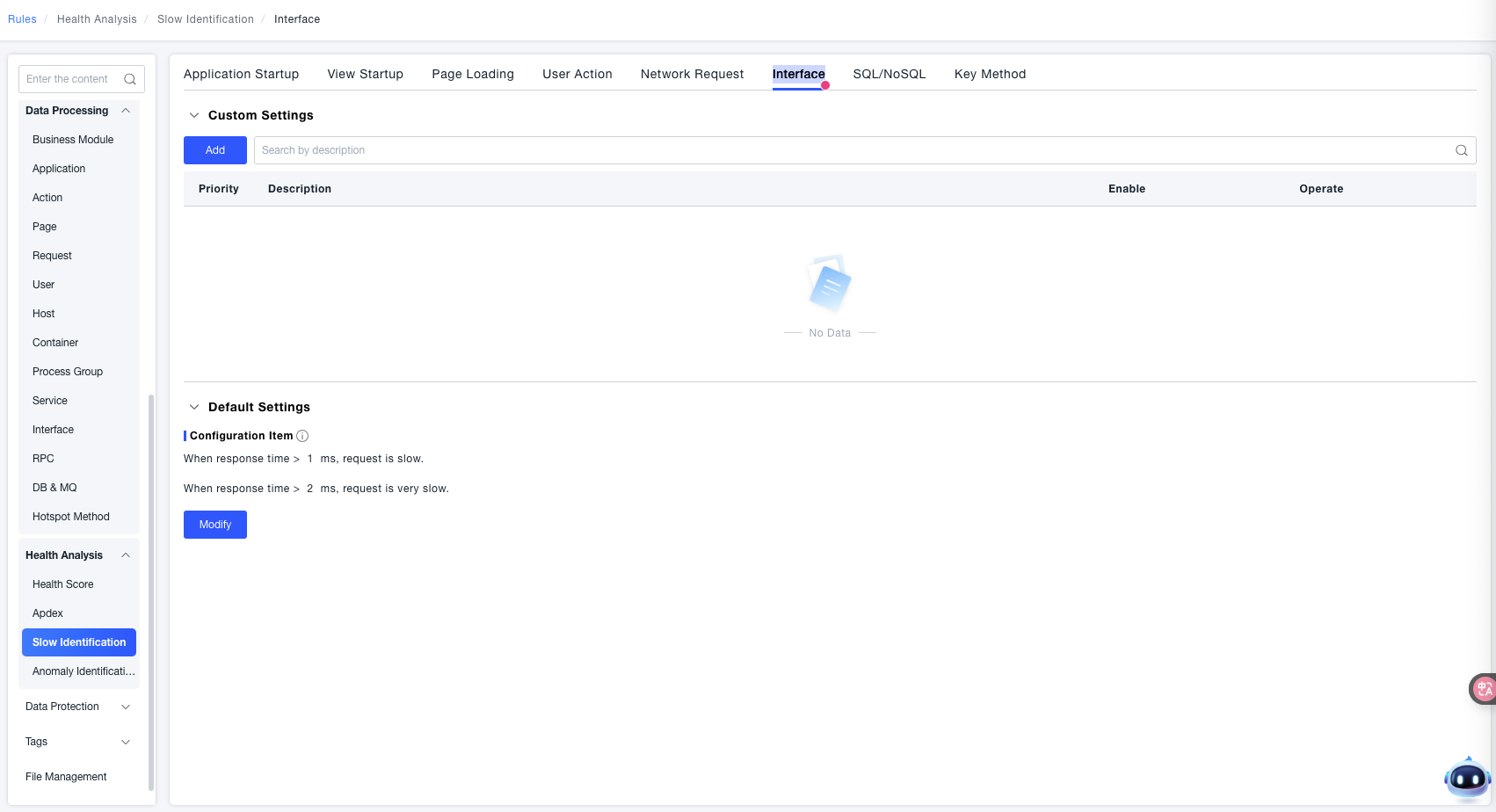
Custom Settings: Custom Settings allow configuring the response time threshold for service interfaces for a specific application.
SQL Statements / NoSQL Operations
Define varying degrees of "Slow Statements" by setting thresholds for "Statement Execution Time".
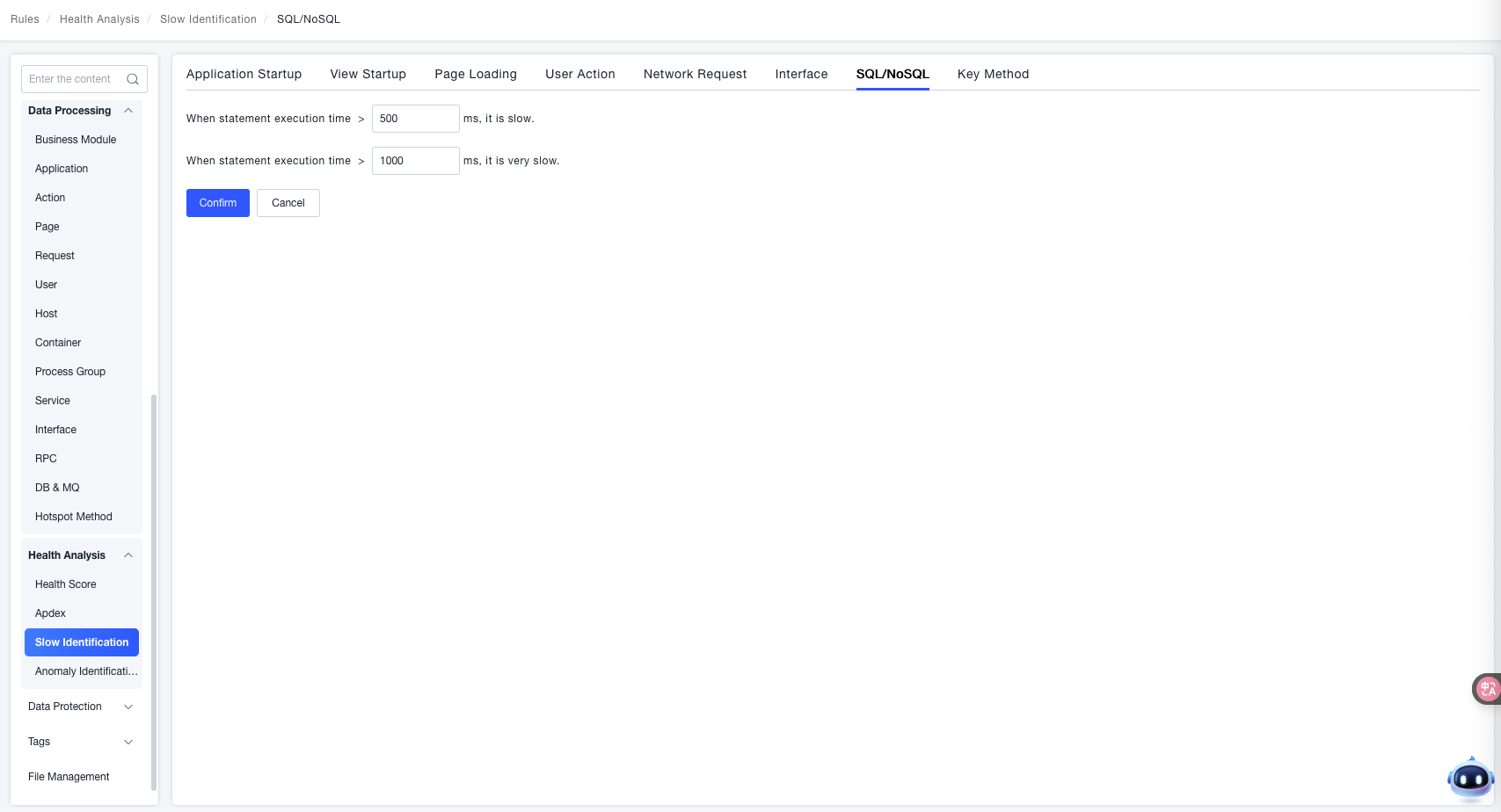
- Slower Statement Execution: When the "Statement Execution Time > Set Threshold" (e.g.,
500 msin the example), it is identified as "Slower Statement Execution". - Very Slow Statement Execution: When the "Statement Execution Time > Set Threshold" (e.g.,
1000 msin the example), it is identified as "Very Slow Statement Execution".
Key Methods
Define varying degrees of "Slow Method Invocation" by setting thresholds for "Method Invocation Time".
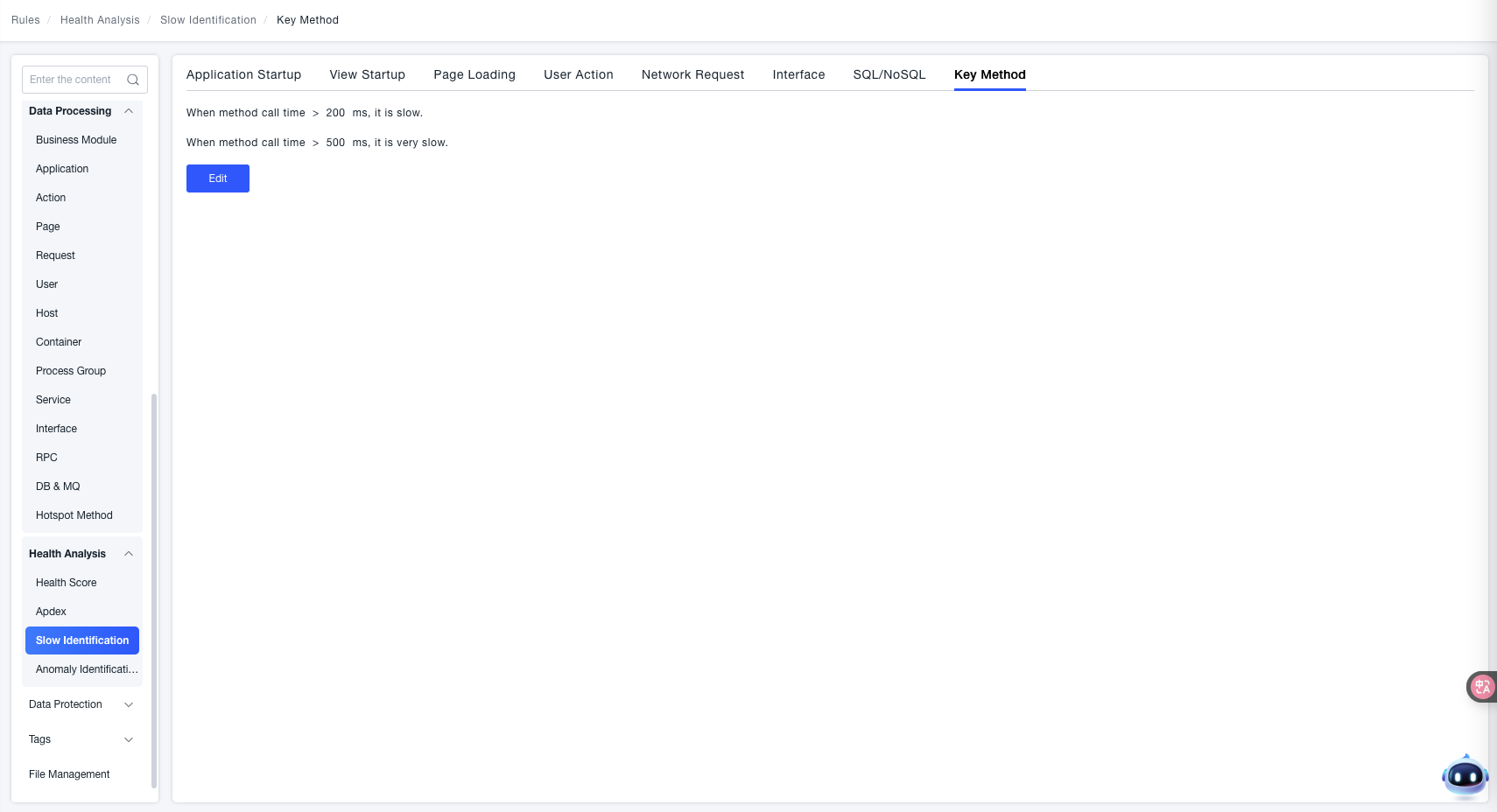
- Slower Method Invocation: When the "Method Invocation Time > Set Threshold" (e.g.,
200 msin the interface example), it is identified as "Slower Method Invocation". - Very Slow Method Invocation: When the "Method Invocation Time > Set Threshold" (e.g.,
500 msin the interface example), it is identified as "Very Slow Method Invocation".